
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
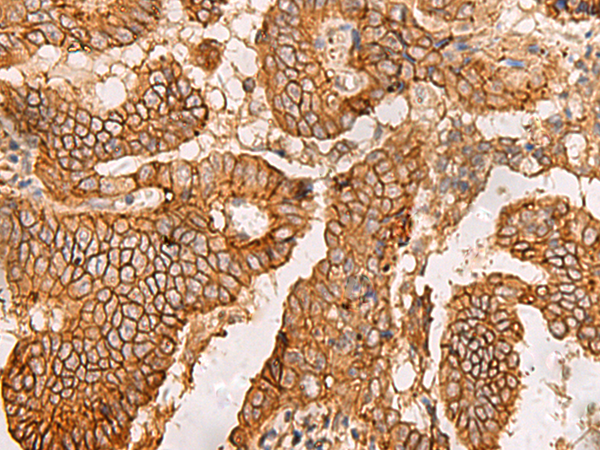
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ESA; KSA; M4S1; MK-1; DIAR5; EGP-2; EGP40; KS1/4; MIC18; TROP1; EGP314; HNPCC8; TACSTD1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human EPCAM |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于EPCAM抗体的代表性文献摘要(虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *EPCAM as a therapeutic target for antibody-drug conjugates in solid tumors*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种新型抗EPCAM抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在结直肠癌和卵巢癌模型中显示出选择性杀伤肿瘤细胞的效果,并验证了EPCAM在转移灶中的高表达特性。
2. **文献名称**: *Dual-labeled anti-EPCAM molecular probes for intraoperative tumor imaging*
**作者**: Wang L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队设计了一种双标记(荧光/放射性核素)抗EPCAM探针,成功应用于小鼠模型和临床前手术导航,显著提高微小肿瘤病灶的术中检出率。
3. **文献名称**: *Epigenetic regulation of EPCAM in circulating tumor cells: Diagnostic implications*
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过分析血液样本中循环肿瘤细胞(CTCs)的EPCAM表达动态,揭示了DNA甲基化调控机制,并开发了基于抗EPCAM抗体的高灵敏度CTC富集检测技术。
---
注:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索关键词如"EPCAM antibody therapeutic/diagnostic"获取。
The epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), also known as CD326. is a transmembrane glycoprotein widely expressed in epithelial tissues. It plays a key role in cell-cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. EpCAM is overexpressed in many epithelial-derived cancers, making it a valuable biomarker for tumor detection and therapeutic targeting. EpCAM antibodies are immunoreagents designed to specifically bind to EpCAM antigens, enabling applications in research, diagnostics, and therapy.
Structurally, EpCAM consists of an extracellular domain with epidermal growth factor (EGF)- and thyroglobulin-like regions, a single transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic tail. Its overexpression in carcinomas correlates with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis. EpCAM antibodies, often monoclonal (e.g., clone Ber-EP4), are routinely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) to identify epithelial origin in cancer diagnostics and distinguish carcinomas from other malignancies. In therapeutics, bispecific EpCAM-targeting antibodies like catumaxomab (with CD3-binding capacity) have been developed to engage immune cells for cancer cell elimination. Additionally, EpCAM antibodies are employed in flow cytometry, circulating tumor cell (CTC) isolation, and as tools to study epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cancer biology. Recent research also explores their role in targeting cancer stem cells. Despite their utility, challenges remain in addressing tumor heterogeneity and minimizing off-target effects in clinical applications.
×