| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
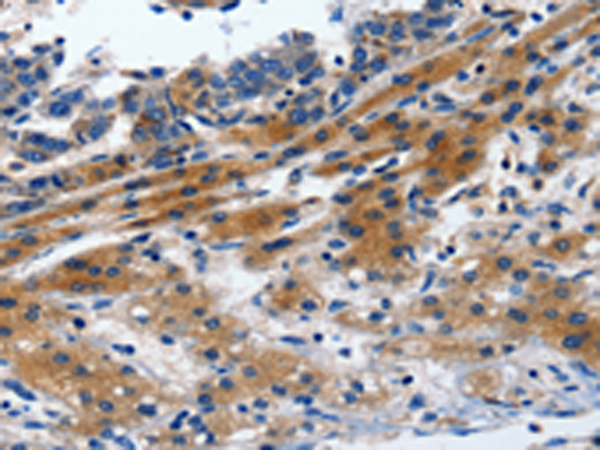
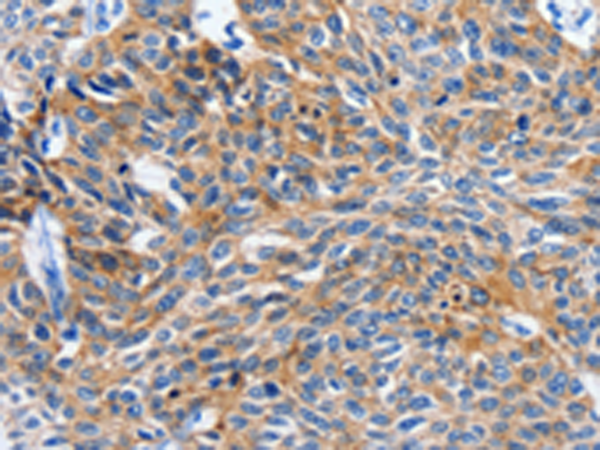
| IHC | 1/15-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD11A, LFA-1, LFA1A |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ITGAL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ITGAL(CD11a)抗体的3篇文献示例,按研究主题分类简要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting LFA-1 (CD11a) in Solid Tumors with Efalizumab: Immune Modulation and Clinical Outcomes*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:探讨抗CD11a单抗(Efalizumab)在实体瘤治疗中的免疫调节作用,发现其通过阻断LFA-1/ICAM-1通路抑制T细胞迁移,但可能增加感染风险。
2. **文献名称**:*CD11a Antibody Attenuates Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease via Inhibiting T Cell Activation*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:研究抗CD11a抗体在骨髓移植模型中的作用,证明其通过抑制T细胞与抗原呈递细胞的黏附,降低急性移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)严重程度。
3. **文献名称**:*ITGAL Gene Variants and Anti-CD11a Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:分析系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者中ITGAL基因多态性与抗CD11a自身抗体的关联,提示其在疾病进展中的潜在生物标志物价值。
---
**备注**:ITGAL编码CD11a蛋白,与CD18组成LFA-1整合素,相关抗体研究多聚焦于免疫疾病治疗(如Efalizumab曾用于银屑病)或实验工具开发。实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar以关键词“ITGAL antibody”或“CD11a antibody”检索近年论文。
The ITGAL antibody targets the protein encoded by the ITGAL gene, which is a subunit (αL, CD11a) of the integrin family. This protein pairs with the β2 subunit (CD18) to form lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1), a cell-surface receptor expressed on leukocytes, including T cells, B cells, and macrophages. LFA-1 plays a critical role in immune responses by mediating cell adhesion and migration through interactions with intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs), particularly ICAM-1. These interactions facilitate immune cell trafficking, antigen presentation, and T-cell activation.
ITGAL antibodies are widely used in research to investigate inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis), and cancer immunotherapy. They help block LFA-1/ICAM binding, enabling studies on immune cell recruitment and inhibition of pathological immune activation. Therapeutic anti-ITGAL antibodies, such as efalizumab, were developed to modulate immune activity but faced limitations due to safety concerns. Current research focuses on optimizing LFA-1-targeted therapies to balance efficacy and side effects. As a tool, ITGAL antibodies remain vital for dissecting integrin signaling pathways and validating therapeutic targets in preclinical models.
×