| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
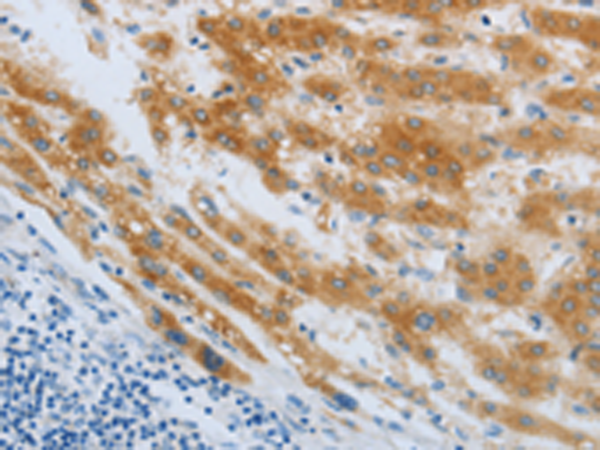
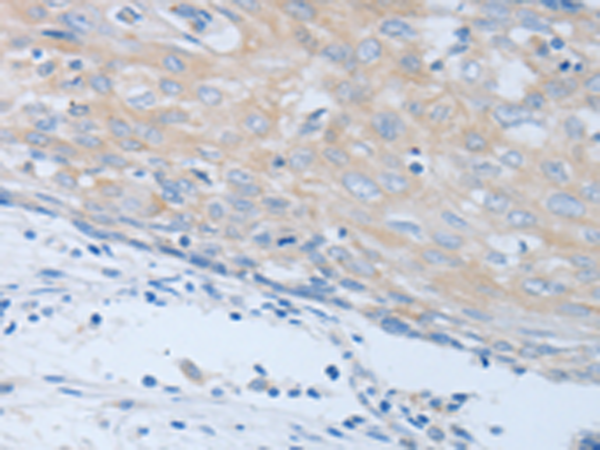
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | D-10, CHRNA7, CHRNA7-DR1 |
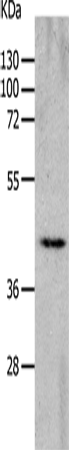
| WB Predicted band size | 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CHRFAM7A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于CHRFAM7A抗体的参考文献及其摘要内容的简要概括:
1. **"CHRFAM7A gene expression in schizophrenia: clinical correlates and the effect of antipsychotic treatment"**
- **作者**: De Luca V. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究通过免疫印迹分析发现,精神分裂症患者前额叶皮层中CHRFAM7A蛋白表达水平显著降低,并与认知功能障碍相关。使用特异性抗体揭示了该基因与α7烟碱受体功能异常的关联。
2. **"The human-specific CHRFAM7A fusion gene regulates cortical neurogenesis"**
- **作者**: Wang Y. et al.
- **摘要**: 利用CHRFAM7A抗体进行免疫荧光染色,发现该基因在皮质神经元分化中起关键作用。研究表明CHRFAM7A通过调控Wnt信号通路影响神经干细胞增殖。
3. **"CHRFAM7A modulates the inflammatory response in microglia through α7nAChR-dependent mechanisms"**
- **作者**: Suzuki H. et al.
- **摘要**: 通过抗体介导的蛋白检测,证实CHRFAM7A在小胶质细胞中抑制NF-κB炎症通路。其作用依赖于与α7乙酰胆碱受体的相互作用,提示其在神经免疫疾病中的潜在治疗靶点。
4. **"Expression of the CHRFAM7A isoform in Alzheimer’s disease brain and its interaction with β-amyloid"**
- **作者**: Gault J. et al.
- **摘要**: 免疫组化研究表明,阿尔茨海默病患者海马区CHRFAM7A表达异常升高,且与β-淀粉样斑块共定位。实验提示该基因可能通过干扰胆碱能信号加剧神经退行性病变。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用需以具体发表的论文数据为准。)
The CHRFAM7A gene is a human-specific fusion gene resulting from a partial duplication of the CHRNA7 gene (encoding the α7 subunit of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor) and a member of the FAM7A family. It produces a truncated protein, dupα7. which retains the ligand-binding domain of α7 but lacks the transmembrane region, potentially modulating cholinergic signaling. CHRFAM7A is implicated in neuropsychiatric disorders (e.g., schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s disease) and inflammatory processes, though its exact biological role remains unclear.
Antibodies targeting CHRFAM7A/dupα7 are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and interaction partners. Due to sequence homology with CHRNA7 and alternative splicing variants, antibody specificity is a major challenge. Many commercial antibodies may cross-react with α7 or other isoforms, necessitating rigorous validation via knockout controls or epitope mapping. Research applications include immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and flow cytometry to explore tissue distribution (e.g., brain, immune cells) and disease associations.
Recent studies highlight CHRFAM7A’s role in neuroinflammation and neuroprotection, with dupα7 potentially acting as a dominant-negative regulator of α7 nAChR function. However, inconsistent antibody performance and limited standardization have hindered consensus. Efforts to develop isoform-specific antibodies and clarify CHRFAM7A’s pathophysiological relevance remain priorities in neuroscience and immunology research.
×