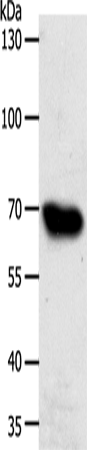
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
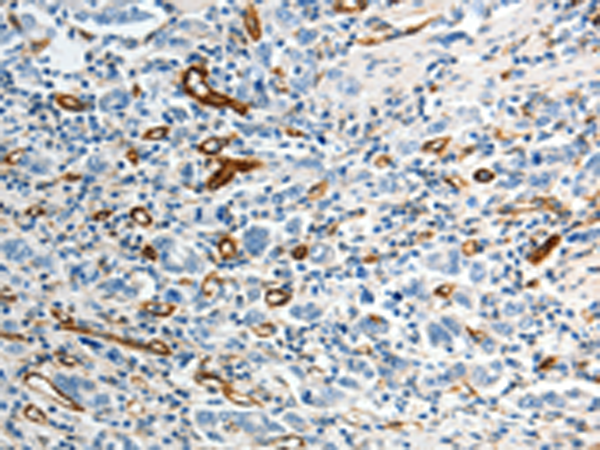
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ABC8; WHITE1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 76 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ABCG1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ABCG1抗体的3篇代表性文献,涵盖其功能、疾病关联及实验应用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*ABCG1 modulates endothelial cell migration and tubulogenesis via regulation of cholesterol homeostasis*
**作者**:Baldán Á, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用ABCG1抗体检测人内皮细胞中ABCG1蛋白表达,发现其通过调节胆固醇外流影响细胞迁移和血管生成,提示其在血管疾病中的潜在作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Macrophage ABCG1 deletion disrupts lipid homeostasis in alveolar macrophages and enhances pulmonary inflammation*
**作者**:Out R, et al.
**摘要**:通过ABCG1抗体染色发现,巨噬细胞特异性敲除ABCG1导致肺泡内脂质堆积,加剧肺部炎症,表明ABCG1在维持肺脂质稳态中的关键性。
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based detection of ABCG1 in human atherosclerotic plaques*
**作者**:Westerterp M, et al.
**摘要**:研究采用ABCG1抗体对动脉粥样硬化斑块进行免疫组化分析,证实ABCG1在斑块巨噬细胞中高表达,并与胆固醇逆转运过程相关,为治疗靶点提供依据。
---
这些研究展示了ABCG1抗体在细胞定位、功能验证及疾病机制探索中的关键应用。
The ABCG1 antibody is a crucial tool in studying the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family, specifically targeting the ABCG1 protein, which plays a vital role in cellular lipid homeostasis. ABCG1. a member of the ABCG subfamily, functions as a transmembrane transporter facilitating cholesterol and phospholipid efflux from cells, particularly macrophages, to high-density lipoprotein (HDL). This process is essential for preventing intracellular lipid accumulation, a key factor in atherosclerosis and metabolic disorders. Structurally, ABCG1 forms a heterodimer and operates as a "half-transporter," requiring dimerization for functionality. Its expression is regulated by liver X receptors (LXRs), linking it to lipid metabolism and inflammation pathways.
ABCG1 antibodies are widely used in research to detect protein expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. They help elucidate ABCG1's role in diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer, where dysregulated lipid metabolism contributes to pathogenesis. Polyclonal and monoclonal variants target specific epitopes (e.g., C-terminal regions), enabling precise localization and functional studies. Recent studies also explore ABCG1's involvement in immune regulation and drug resistance, highlighting its therapeutic potential. However, challenges remain in standardizing antibody specificity across experimental models, necessitating rigorous validation. Overall, ABCG1 antibodies are indispensable for advancing understanding of lipid transport mechanisms and their disease implications.
×