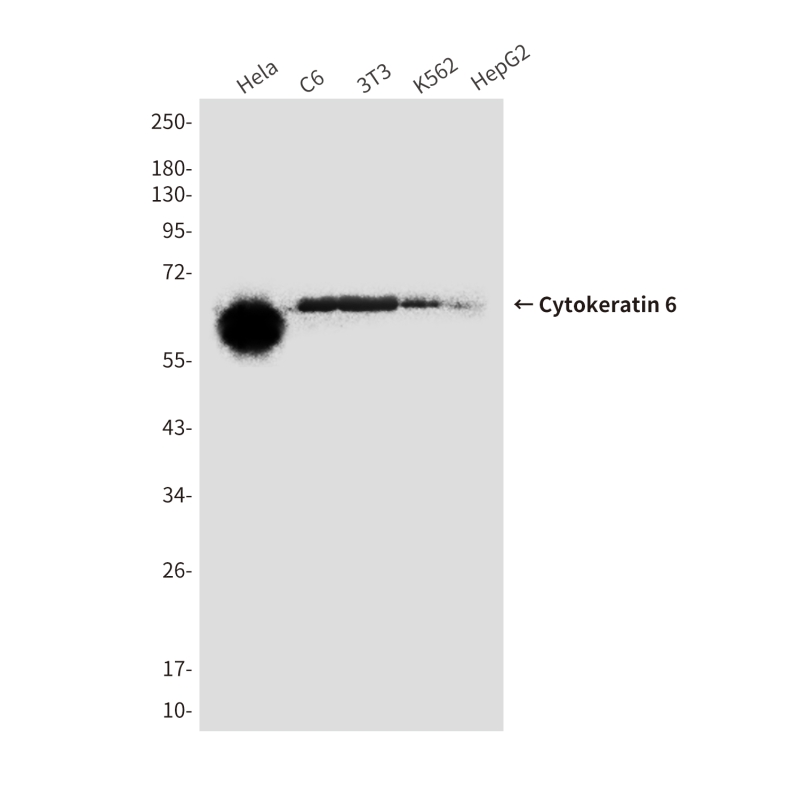
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
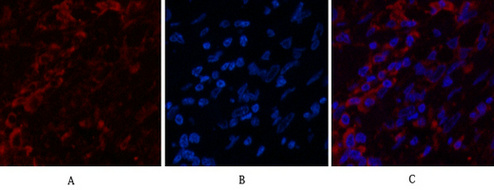
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
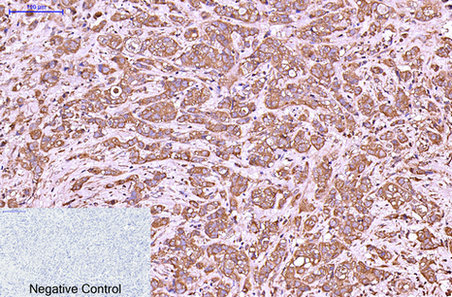
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CK 6A; CK 6B; CK 6C; CK 6D; CK 6E; CK-6C; CK-6E; K6a keratin; K6b keratin; K6C; K6c keratin; K6d keratin; K6e keratin; Keratin; KRT6A; KRT6B; KRT6C; KRT6D; KRT6E |
| Entrez GeneID | 3853/3854/286887 |
| clone | 1C5 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 60 kDa; Observed MW: 56-60 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide of Cytokeratin 6 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ADIPOR1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects"
**作者**: Yamauchi, T., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次克隆并鉴定了ADIPOR1和ADIPOR2两种脂联素受体,通过特异性抗体证实两者在肌肉和肝脏中的差异表达,揭示了其在调节胰岛素敏感性和脂肪酸氧化中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Crystal structure of the adiponectin receptor (ADIPOR1) and its ligand binding mechanism"
**作者**: Tanabe, H., et al.
**摘要**: 利用X射线晶体学解析了ADIPOR1的三维结构,并通过抗体结合实验验证其细胞膜定位及与脂联素相互作用的结构域,为靶向受体设计提供了分子基础。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Adiponectin receptor 1 regulates mitochondrial function in human skeletal muscle"
**作者**: Hug, C., et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过免疫印迹(Western blot)和免疫组化(IHC)技术,使用ADIPOR1抗体证明其在骨骼肌线粒体中的富集,并发现其缺失导致线粒体功能障碍,与胰岛素抵抗相关。
---
4. **文献名称**: "ADIPOR1 mutations are associated with diabetic nephropathy via altered ceramide metabolism"
**作者**: Mao, X., et al.
**摘要**: 该文献通过ADIPOR1抗体检测肾脏组织中受体表达水平,发现其基因突变导致神经酰胺代谢异常,进而促进糖尿病肾病的病理进展。
---
这些研究均利用ADIPOR1抗体进行蛋白定位、表达分析或功能验证,涵盖基础结构解析至疾病机制探索。
ADIPOR1 (Adiponectin Receptor 1) is a cell membrane protein that binds adiponectin, a hormone involved in regulating glucose metabolism, fatty acid oxidation, and insulin sensitivity. As a key component of metabolic signaling pathways, ADIPOR1 activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), promoting energy homeostasis and anti-inflammatory responses. Dysregulation of ADIPOR1 expression or function has been linked to metabolic disorders, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases, making it a significant target for biomedical research.
ADIPOR1 antibodies are essential tools for studying the receptor's expression, localization, and molecular interactions. These antibodies are typically developed using immunogenic peptides derived from specific regions of the human ADIPOR1 protein (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal domains) and validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry. High-quality ADIPOR1 antibodies demonstrate specificity through knockout validation or siRNA-mediated silencing controls, ensuring reliable detection in tissues like skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue where the receptor is abundantly expressed.
In research, ADIPOR1 antibodies help elucidate mechanisms underlying metabolic diseases and evaluate therapeutic interventions targeting adiponectin signaling. They also aid in exploring ADIPOR1's role in cancer progression, neurodegenerative disorders, and aging-related pathologies. Commercial antibodies often include recombinant proteins or epitope tags to enhance reproducibility, supporting both basic and translational studies aimed at understanding metabolic regulation and developing precision therapies.
×