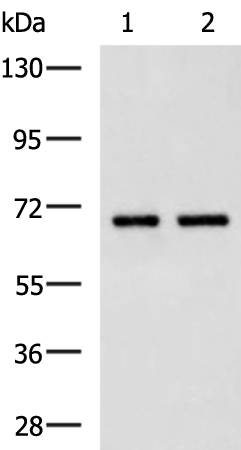
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
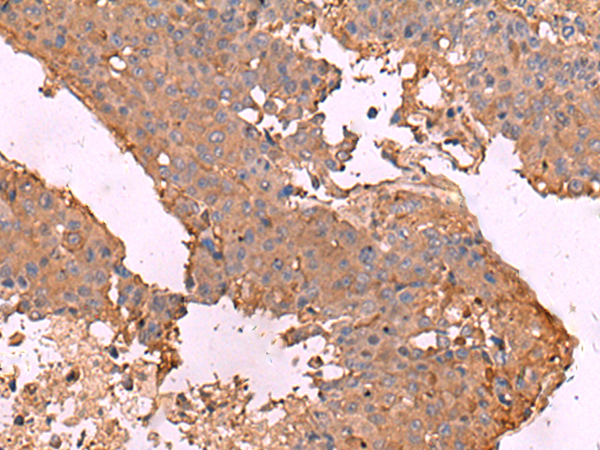
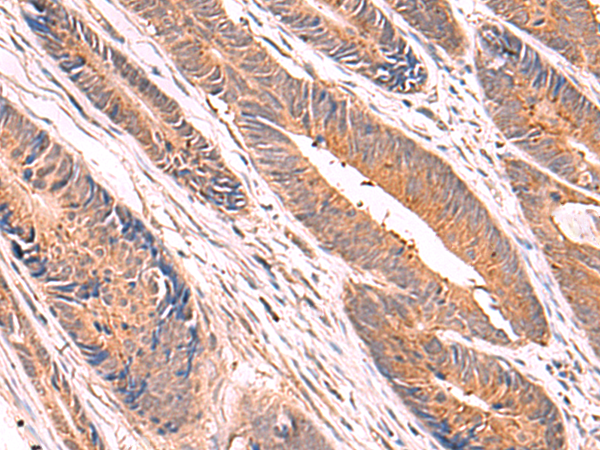
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 87 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ITGB7 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ITGB7抗体的3篇参考文献示例,涵盖其在免疫调节和疾病模型中的作用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*α4β7 integrin mediates lymphocyte binding to the mucosal vascular addressin MAdCAM-1*
**作者**:Berlin, C., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过抗β7抗体阻断实验,证实了α4β7整合素在介导淋巴细胞与肠道黏膜地址素MAdCAM-1结合中的关键作用,揭示了β7亚基在肠道淋巴细胞归巢中的重要性。
2. **文献名称**:*Integrin αEβ7 mediates adhesion of T lymphocytes to epithelial cells*
**作者**:Cepek, K.L., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用抗β7抗体阻断αEβ7整合素功能,证明其在调节T细胞与肠道上皮细胞黏附中的作用,为黏膜免疫中T细胞滞留机制提供了证据。
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting β7 integrin reduces leukocyte recruitment and fibrosis in experimental colitis*
**作者**:Picarella, D., et al.
**摘要**:在小鼠结肠炎模型中,抗β7抗体显著减少了炎症细胞浸润和肠道纤维化,提示靶向ITGB7可能成为炎症性肠病(IBD)的治疗策略。
---
**备注**:多数研究针对α4β7或αEβ7复合体,但均涉及ITGB7亚基的功能。直接靶向ITGB7的独立抗体研究较少,上述文献通过阻断β7亚基阐明其在病理生理中的作用。
The integrin β7 subunit (ITGB7) is a critical component of heterodimeric cell adhesion receptors that mediate interactions between immune cells and their microenvironment. It pairs with α4 or αE subunits to form integrins α4β7 and αEβ7. respectively. These receptors play pivotal roles in lymphocyte homing to gut-associated lymphoid tissues (GALT) and mucosal immunity. α4β7 binds to mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) on endothelial cells, directing lymphocyte trafficking to intestinal sites, while αEβ7 interacts with E-cadherin on epithelial cells, promoting intraepithelial lymphocyte retention.
ITGB7 antibodies are research and therapeutic tools targeting these pathways. In inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and other gut-related disorders, blocking α4β7-MAdCAM-1 interactions with anti-ITGB7 antibodies (e.g., vedolizumab) has shown efficacy in reducing inflammation by inhibiting lymphocyte infiltration. Similarly, αEβ7 is implicated in pathologies involving epithelial inflammation and cancer metastasis.
Research on ITGB7 antibodies extends to autoimmune diseases, cancer immunotherapy, and understanding immune cell migration mechanisms. Therapeutic strategies aim to balance immune suppression with site-specific targeting to minimize systemic side effects. Current studies also explore biomarkers for patient stratification and combination therapies. ITGB7 remains a key focus in developing precision therapies for mucosal immunity dysregulation.
×