| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
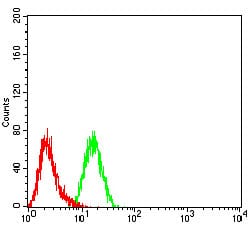
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
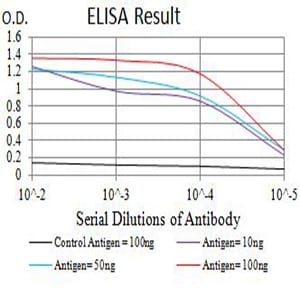
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CSF3R; SCN7; GCSFR |
| Entrez GeneID | 1441 |
| clone | 3G10G2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 92.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD114 (AA: extra 25-187) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD114(G-CSFR)抗体相关的文献摘要概括:
1. **"Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor signaling and its role in myeloid disorders"**
作者:Dong F, Bouscary D
摘要:探讨G-CSFR(CD114)在正常造血和骨髓异常增生中的作用,分析其抗体在白血病细胞信号通路研究中的应用,揭示受体突变与治疗耐药性的关联。
2. **"Targeting the G-CSF receptor in acute myeloid leukemia: antibody-based therapeutic strategies"**
作者:Smith C, et al.
摘要:评估抗CD114单克隆抗体在AML治疗中的潜力,通过体外实验证明抗体可抑制白血病细胞增殖并增强化疗药物敏感性,提出靶向治疗新方向。
3. **"Structural characterization of the G-CSF receptor complex using monoclonal antibodies"**
作者:Yoshikawa A, et al.
摘要:利用特异性CD114抗体解析G-CSFR胞外结构域构象,揭示受体二聚化机制,为开发靶向受体激活/抑制功能的治疗性抗体提供结构依据。
注:实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索确认,以上为模拟概括。
CD114. also known as the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor α subunit (GM-CSFRα or CSF2RA), is a cell surface protein that forms part of the receptor complex for GM-CSF, a cytokine critical for hematopoiesis and immune regulation. The CD114 antibody specifically targets this subunit, enabling researchers to study GM-CSF signaling pathways and receptor expression in various contexts. GM-CSF binding to CD114 triggers dimerization with the β subunit (CD131), activating downstream JAK-STAT, MAPK, and PI3K pathways that regulate myeloid cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
CD114 antibodies are widely used in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting to analyze receptor distribution and density on hematopoietic cells, including granulocytes, monocytes, and macrophages. These tools have revealed CD114's role in both physiological processes (e.g., infection response) and pathological conditions. Elevated CD114 expression is associated with certain leukemias, autoimmune disorders, and chronic inflammation, making it a potential diagnostic marker or therapeutic target. Neutralizing CD114 antibodies are also explored for blocking GM-CSF signaling in inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
Research applications extend to understanding myeloid cell development, cytokine crosstalk, and receptor trafficking. Commercially available CD114 antibodies vary in clonality (monoclonal/polyclonal), species reactivity, and conjugation formats, requiring validation for specific experimental models. Recent studies also investigate CD114's involvement in tumor microenvironment modulation and immunotherapy resistance.
×