| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
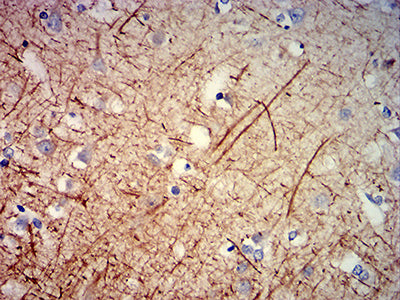
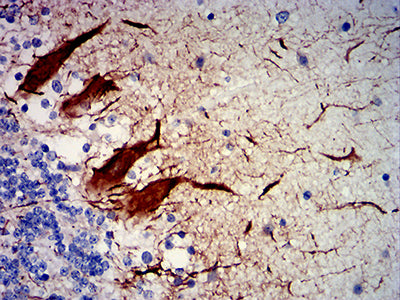
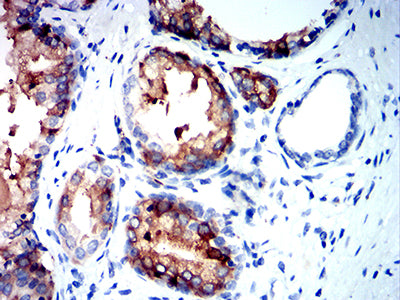
| IHC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
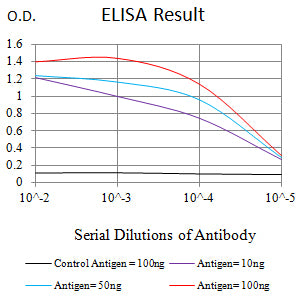
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NFH; CMT2CC |
| Entrez GeneID | 4744 |
| clone | 2C12F3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 112.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human NEFH (AA: 2-251) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于NEFH抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **《Neurofilament heavy chain antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid as a biomarker for neurodegeneration》**
- **作者**:Teunissen CE, et al.
- **摘要**:该研究探讨了脑脊液中神经丝重链(NEFH)抗体作为神经退行性疾病(如阿尔茨海默病和多发性硬化症)生物标志物的潜力,发现其水平与神经元损伤程度相关。
2. **《Autoantibodies to neurofilament heavy chain in paraneoplastic neuropathy》**
- **作者**:Stork AC, et al.
- **摘要**:研究发现,副肿瘤性周围神经病变患者血清中存在针对NEFH的自身抗体,提示NEFH抗体可能与癌症相关的神经免疫反应有关。
3. **《Neurofilament heavy chain phosphorylation regulates axon integrity and disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis》**
- **作者**:Ayers JI, et al.
- **摘要**:通过动物模型和患者样本分析,揭示了NEFH磷酸化异常在肌萎缩侧索硬化症(ALS)中的病理作用,并验证了针对NEFH的抗体在疾病诊断中的应用价值。
以上文献均聚焦于NEFH抗体在神经系统疾病中的诊断、病理机制或生物标志物研究。
The neurofilament heavy polypeptide (NEFH) antibody is a tool used to detect NEFH, a key component of neuronal intermediate filaments. Neurofilaments, composed of light (NEFL), medium (NEFM), and heavy (NEFH) subunits, form the structural scaffold of neurons, maintaining axonal integrity and regulating diameter. NEFH, the largest subunit (~200 kDa), contains a unique carboxy-terminal tail domain critical for filament cross-linking and cytoskeletal organization.
NEFH antibodies are widely employed in neuroscience research to study neuronal health, axonal transport, and neurodegeneration. They help visualize neurofilament distribution in tissues via immunohistochemistry or measure NEFH levels in biofluids (e.g., cerebrospinal fluid, blood) using immunoassays. Elevated NEFH in biofluids often indicates axonal damage, linking it to neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., ALS, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s), traumatic brain injury, or multiple sclerosis.
Commercial NEFH antibodies are typically monoclonal or polyclonal, targeting specific epitopes (e.g., phosphorylated or non-phosphorylated regions). Specificity validation is crucial due to cross-reactivity risks with other neurofilament subunits. Recent advances in ultrasensitive assays, like Simoa, have enhanced NEFH detection as a biomarker for early neurodegeneration. Despite its utility, interpreting NEFH levels requires context, as increases may reflect acute injury or chronic disease progression. Ongoing research aims to standardize its use in clinical diagnostics and therapeutic monitoring.
×