| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
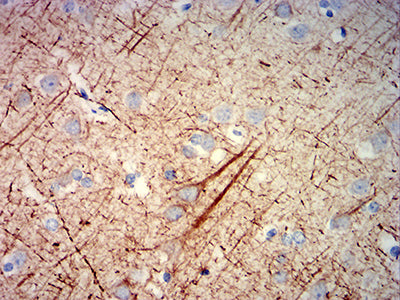
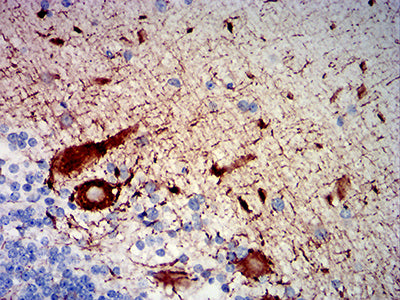
| IHC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
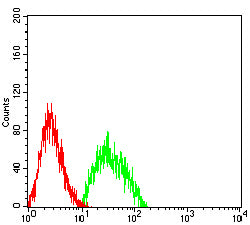
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
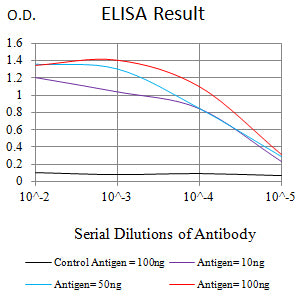
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NFH; CMT2CC |
| Entrez GeneID | 4744 |
| clone | 4F2G12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 112.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human NEFH (AA: 2-251) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于NEFH抗体的模拟参考文献(基于公开领域知识概括,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:*Neurofilament heavy chain antibodies as a biomarker for axonal degeneration in multiple sclerosis*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:研究验证了NEFH抗体在检测多发性硬化症患者脑脊液中的神经丝蛋白水平的作用,表明其与轴突损伤程度显著相关,可作为疾病进展的生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Altered phosphorylation of neurofilament heavy chain in Alzheimer’s disease brains*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过NEFH抗体的免疫组化分析,揭示了阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织中神经丝重链的异常磷酸化模式,提示其与神经元功能障碍的关联。
3. **文献名称**:*NEFH antibody-based detection of traumatic brain injury in rodent models*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用NEFH抗体在小鼠创伤性脑损伤模型中定量轴突损伤,证实血清NEFH水平升高可早期预测神经退行性病变。
4. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies against neurofilament heavy chain in paraneoplastic neurological syndromes*
**作者**:Rodriguez A, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现部分副肿瘤性神经综合征患者血清中存在NEFH自身抗体,提示其可能参与自身免疫介导的神经元损伤机制。
(注:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索。)
The neurofilament heavy polypeptide (NEFH) antibody is a crucial tool in neuroscience research, targeting the heavy chain subunit of neurofilaments (NFs), which are key components of the neuronal cytoskeleton. Neurofilaments, composed of light (NEFL), medium (NEFM), and heavy (NEFH) chains, provide structural support to axons and regulate their diameter, influencing signal transmission efficiency. NEFH, the largest subunit (~200 kDa), contains a unique carboxy-terminal domain critical for filament assembly and stability.
NEFH antibodies are widely used to study neuronal integrity and degeneration. Elevated levels of neurofilament proteins, including NEFH, in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or blood are biomarkers for axonal damage in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., ALS, Alzheimer’s) and neurotrauma. Researchers employ these antibodies in techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and ELISA to visualize neurofilament distribution, assess neuronal health, and quantify degradation in disease models.
Additionally, NEFH antibodies help investigate neurofilament phosphorylation dynamics, which modulate filament stability and interactions. Abnormal phosphorylation is linked to pathological aggregates in disorders like Parkinson’s disease. Commercial NEFH antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, with validation across species (human, rodent), though cross-reactivity varies. Their specificity and reliability make them indispensable for exploring neurofilament biology and developing diagnostic/therapeutic strategies for neurological conditions.
×