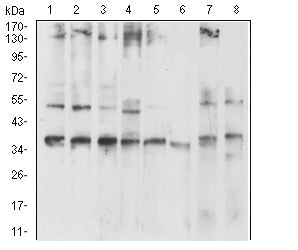
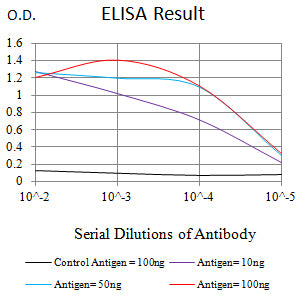
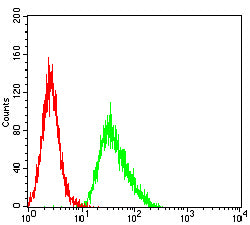
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TNFRSF9; ILA; 4-1BB; CDw137 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3604 |
| clone | 2A12C2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD137 (AA: 214-255) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD137抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Agonist Anti-CD137 mAb Acts on Myeloid Dendritic Cells to Break Peripheral Tolerance"
**作者**: Bartkowiak, T., Curran, M.A.
**摘要**: 该研究揭示了激动型CD137抗体通过作用于骨髓来源的树突状细胞(而非直接激活T细胞),打破免疫耐受并增强抗肿瘤免疫应答。实验表明,CD137激动剂可促进抗原提呈细胞的成熟和交叉呈递能力,为联合免疫治疗提供了机制支持。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Phase I Study of Urelumab (BMS-663513), a CD137 Agonist Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors"
**作者**: Segal, N.H., et al.
**摘要**: 这篇临床I期试验评估了Urelumab(一种CD137激动型抗体)在晚期实体瘤患者中的安全性和初步疗效。结果显示,药物在部分患者中诱导了持久的抗肿瘤反应,但高剂量组出现肝毒性,提示需优化剂量方案以平衡疗效与副作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: "CD137-Directed Bispecific T-Cell Engagers for Tumor Immunotherapy"
**作者**: Hinner, M.J., et al.
**摘要**: 研究设计了一种双特异性抗体,同时靶向CD137和肿瘤相关抗原(如HER2)。该抗体通过局部激活CD137信号增强T细胞对肿瘤的特异性杀伤,同时减少全身性免疫激活带来的副作用,为靶向实体瘤提供了新策略。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对来源及细节。CD137抗体的研究重点包括联合疗法(如PD-1抑制剂)、剂量依赖性毒性(如肝损伤)及新型工程化抗体开发。
CD137 (4-1BB), a member of the TNF receptor superfamily, is a co-stimulatory molecule expressed on activated T cells, NK cells, and other immune cells. Its engagement with CD137 ligand (CD137L) provides secondary signals that enhance T cell proliferation, survival, and cytokine production, making it a promising target for cancer immunotherapy. First identified in the 1990s, CD137 gained attention for its role in amplifying anti-tumor immune responses, particularly in preclinical models where CD137 agonists showed potent antitumor activity.
Therapeutic CD137-targeting antibodies, designed to mimic natural ligand interactions, emerged as a strategy to boost immune activation. Early agonists like urelumab (BMS-663513) and utomilumab (PF-05082566) demonstrated antitumor efficacy in clinical trials but faced challenges. Urelumab showed hepatotoxicity at higher doses, leading to dose-limiting issues, while utomilumab, though safer, exhibited more modest clinical activity. These findings highlighted the delicate balance between immune activation and toxicity in targeting CD137.
Recent efforts focus on optimizing CD137 antibodies through engineering (e.g., Fc domain modifications to fine-tune receptor clustering) or combining them with checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1/PD-L1) to enhance synergistic effects. Bispecific antibodies simultaneously targeting CD137 and tumor-associated antigens are also being explored to improve tumor-specific T cell activation while reducing systemic toxicity. Despite challenges, CD137 remains a key candidate in next-generation immuno-oncology therapies.
×