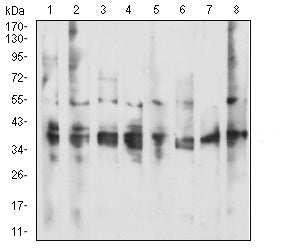
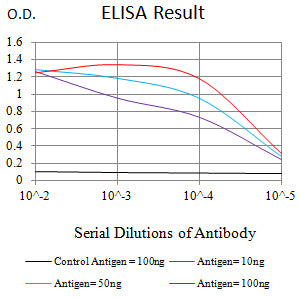
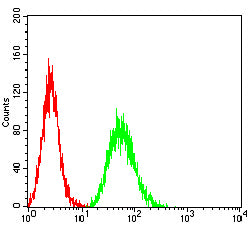
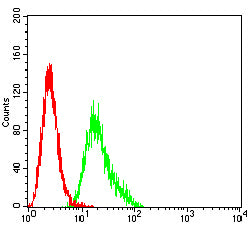
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TNFRSF9; ILA; 4-1BB; CDw137 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3604 |
| clone | 2C6B4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD137 (AA: 214-255) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD137抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"CD137 stimulation enhances the antileukemic effect of T cells with dual CD19/CD123 chimeric antigen receptors*"
**作者**:Zhang et al. (2020)
**摘要**:研究探讨了CD137(4-1BB)共刺激信号在双靶向CAR-T细胞治疗白血病中的作用,发现CD137抗体可增强CAR-T细胞的增殖能力与肿瘤清除效果,同时减少耗竭表型。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Therapeutic activity of agonistic monoclonal antibodies against CD137 in immunocompetent tumor-bearing mice*"
**作者**:Melero et al. (1997)
**摘要**:早期经典研究,首次证明CD137激动型抗体通过激活T细胞和增强抗肿瘤免疫应答,显著抑制小鼠肿瘤生长,为后续临床开发奠定基础。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Phase I study of CD137 agonistic antibody urelumab in combination with nivolumab in advanced solid tumors*"
**作者**:Segal et al. (2019)
**摘要**:临床试验报道了CD137抗体(urelumab)与PD-1抑制剂联用的安全性及初步疗效,部分患者肿瘤缓解,但需注意剂量相关的肝毒性风险。
---
**扩展机制研究**:
4. **文献名称**:*"CD137 promotes proliferation and survival of human breast cancer cells by modulating mitochondrial dynamics*"
**作者**:Bartkowiak et al. (2018)
**摘要**:揭示了CD137信号通过调控线粒体动态平衡促进肿瘤细胞存活的新机制,提示需谨慎设计靶向CD137的疗法以避免潜在促癌风险。
---
这些研究覆盖了CD137抗体的治疗潜力、机制探索及临床转化挑战。如需具体文献链接或补充,可进一步说明。
CD137 (4-1BB), a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, is a costimulatory immune checkpoint molecule primarily expressed on activated T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells. Its interaction with the ligand CD137L triggers signaling pathways that enhance T-cell proliferation, survival, and cytotoxic activity, making it a compelling target for cancer immunotherapy. CD137 agonists, including monoclonal antibodies, are designed to amplify antitumor immune responses by stimulating CD137-positive immune cells. Preclinical studies demonstrated that CD137-targeting antibodies promote tumor regression in murine models, particularly when combined with other therapies like PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors or adoptive cell transfer.
The first-generation anti-CD137 antibodies, such as Utomilumab (PF-05082566) and Urelumab (BMS-663513), entered clinical trials in the 2010s. While Urelumab showed potent immune activation, its development was hampered by dose-limiting hepatotoxicity. Utomilumab, with a weaker agonistic effect, exhibited better tolerability but modest monotherapy efficacy. These findings highlighted the delicate balance between therapeutic potency and toxicity, influenced by factors like antibody epitope specificity, Fc receptor interactions, and dosing regimens. Current research focuses on optimizing CD137 agonists through bispecific antibodies (e.g., targeting tumor antigens), combination therapies, or localized delivery to minimize systemic toxicity. Additionally, structural engineering of antibodies to fine-tune CD137 clustering and signaling intensity is being explored to enhance therapeutic windows. Despite challenges, CD137 remains a promising target in next-generation immuno-oncology strategies.
×