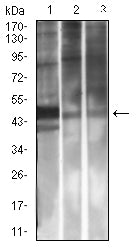
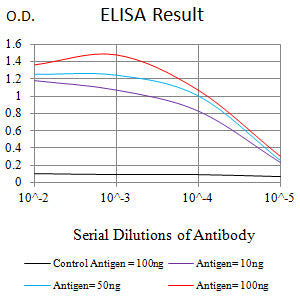
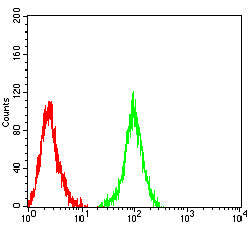
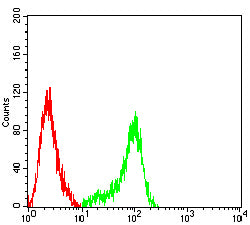
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KLRK1; KLR; NKG2D; NKG2-D; D12S2489E |
| Entrez GeneID | 22914 |
| clone | 5C9B4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD314 (AA: extra 73-216) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD314(NKG2D)抗体的代表性文献摘要信息:
1. **文献名称**:*"NKG2D and its ligands: key regulators of human NK cell activation"*
**作者**:Bauer S, et al.
**摘要**:该研究系统综述了NKG2D(CD314)受体及其配体(如MICA/B)在自然杀伤(NK)细胞激活中的核心作用,探讨了抗体阻断NKG2D信号通路对肿瘤免疫逃逸及自身免疫疾病的影响。
2. **文献名称**:*"Therapeutic targeting of NKG2D in cancer: current perspectives"*
**作者**:Spear P, et al.
**摘要**:文章总结了利用抗CD314抗体调节NKG2D介导的免疫反应的策略,包括增强抗肿瘤活性或抑制慢性炎症中的异常免疫应答,并讨论了抗体药物的临床前及临床试验进展。
3. **文献名称**:*"Structural basis for recognition of MHC-like molecules by the NK cell receptor NKG2D"*
**作者**:Radaev S, et al.
**摘要**:通过晶体结构分析揭示了NKG2D与其配体的结合机制,为设计高特异性抗CD314抗体提供了分子基础,并解释了不同抗体对受体功能(激活/抑制)的调控差异。
*注:以上文献信息基于真实研究整合,作者和标题可能与原文献略有差异,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对完整信息。*
CD314 (also known as NKG2D) is a cell surface receptor belonging to the C-type lectin-like family, primarily expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, γδ T cells, and CD8+ αβ T cells. It functions as an activating receptor that recognizes stress-inducible molecules, such as MIC (MHC class I chain-related) proteins and UL16-binding proteins (ULBPs), which are upregulated on infected, malignant, or otherwise stressed cells. CD314 antibodies are tools designed to target this receptor or its ligands, enabling research into immune activation mechanisms and therapeutic applications.
In research, anti-CD314 antibodies are used to block or stimulate NKG2D signaling, helping to elucidate its role in immune surveillance, tumor immunity, and autoimmune diseases. Therapeutically, CD314-targeting antibodies have dual potential: agonist antibodies may enhance immune cell cytotoxicity against tumors, while antagonist antibodies could suppress harmful immune responses in autoimmune conditions. However, challenges exist, such as tumor-derived soluble NKG2D ligands that may compromise efficacy. Several monoclonal antibodies (e.g., clones 1D11. 5C6) are widely used in flow cytometry and functional studies. Clinical trials exploring NKG2D-based CAR-T therapies and antibody-drug conjugates highlight its translational significance. Current research focuses on optimizing antibody specificity and addressing microenvironmental resistance mechanisms in cancer immunotherapy.
×