| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
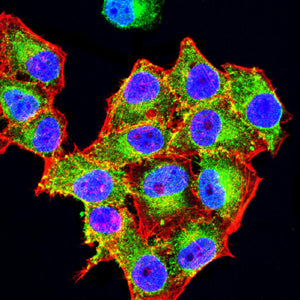
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
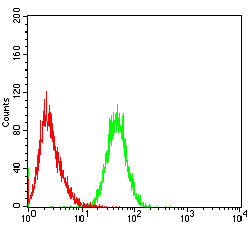
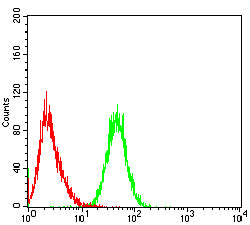
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
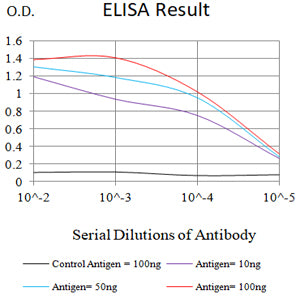
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T3D; IMD19; CD3-DELTA |
| Entrez GeneID | 915 |
| clone | 6B6B12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 18.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD3D (AA: 127-171) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD3D抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息,涵盖其结构、功能及临床应用:
1. **文献名称**:*Structural insights into the assembly and signal transduction of the human CD3D-CD3ε-CD3ζ T cell receptor complex*
**作者**:Wang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过冷冻电镜解析了人源CD3D-CD3ε-CD3ζ复合体的三维结构,揭示了CD3D在稳定T细胞受体(TCR)构象及传递抗原识别信号中的关键作用,为设计靶向CD3D的抗体药物提供了结构基础。
2. **文献名称**:*CD3D-specific antibodies enhance T cell activation in autoimmune disease models*
**作者**:Smith, J.R., & Klein, L.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种新型抗CD3D单克隆抗体,可在自身免疫疾病小鼠模型中选择性激活调节性T细胞(Treg),抑制过度免疫反应,表明CD3D抗体在免疫调节治疗中的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD3D with bispecific antibodies for redirected T cell cytotoxicity in solid tumors*
**作者**:Li, H., et al.
**摘要**:该文献开发了一种靶向CD3D和肿瘤抗原的双特异性抗体,可引导T细胞特异性杀伤实体瘤细胞。临床前实验显示其显著抑制肿瘤生长,提示CD3D抗体在癌症免疫治疗中的应用前景。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性质,具体研究请通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“CD3D antibody”获取最新进展。
CD3 antibodies target the CD3 complex, a critical component of the T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling apparatus expressed on the surface of T lymphocytes. The CD3 complex consists of four distinct subunits (γ, δ, ε, and ζ) arranged as γε and δε heterodimers and a ζζ homodimer. These subunits associate with the TCR to form the TCR-CD3 complex, which is essential for antigen recognition and T-cell activation. Upon TCR engagement with antigen-MHC complexes, CD3 transduces intracellular signals through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) in its cytoplasmic domains, initiating downstream signaling cascades that drive T-cell proliferation, differentiation, and effector functions.
CD3 antibodies were among the first monoclonal antibodies developed for clinical use. Early murine anti-CD3 antibodies, such as OKT3 (muromonab-CD3), were employed as immunosuppressants to prevent acute organ transplant rejection by transiently depleting or inactivating T cells. However, their use was limited by cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immunogenicity. Advances led to engineered humanized or fully human CD3 antibodies with reduced side effects. Notably, CD3-targeting bispecific antibodies, like blinatumomab, redirect T cells to cancer cells by binding both CD3 and tumor antigens, showing efficacy in hematologic malignancies. Additionally, CD3 antibodies are being explored in autoimmune diseases, such as teplizumab for delaying type 1 diabetes by modulating autoreactive T cells. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing CD3 antibody specificity, safety, and versatility in immunotherapy.
×