| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
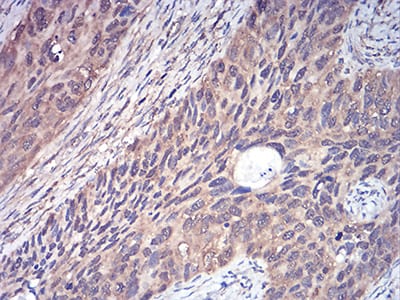
| IHC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
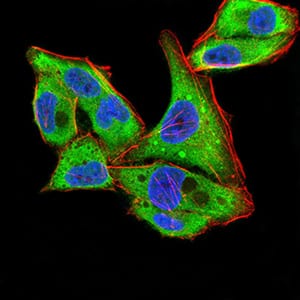
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
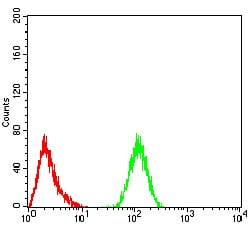
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
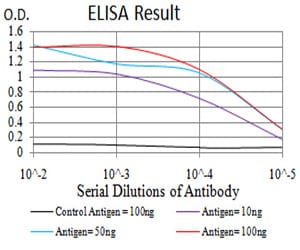
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HS1; GW128; YWHAA; KCIP-1; HEL-S-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7529 |
| clone | 3D2E10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human YWHAB (AA: 1-246) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD99抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要:
1. **"CD99 is a key marker for the diagnosis of Ewing sarcoma" by Folpe, A.L. et al.**
该研究通过免疫组化分析,证实CD99抗体在尤文肉瘤诊断中的高敏感性和特异性,可用于与其他小圆细胞肿瘤的鉴别。
2. **"CD99 regulates T cell migration via homotypic interaction" by Dworzak, M.N. et al.**
研究发现CD99抗体阻断实验显著抑制T细胞的跨内皮迁移,提示CD99在免疫细胞迁移中的关键作用及其可能的治疗干预靶点。
3. **"CD99 expression in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Prognostic implications" by Ramakrishnan, R. et al.**
文章评估CD99抗体在急性淋巴细胞白血病(ALL)中的表达模式,发现高表达与不良预后相关,支持其作为潜在生物标志物的价值。
(注:上述文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需核实具体来源及细节。)
CD99 antibody targets the CD99 antigen, a 32 kDa cell surface glycoprotein encoded by the *MIC2* gene. Initially identified in the 1980s, CD99 is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues, particularly in hematopoietic cells, endothelial cells, and certain epithelial cells. It plays dual roles in cellular adhesion and migration, modulating processes like T-cell activation, apoptosis, and leukocyte transendothelial migration. Structurally, CD99 exists as two isoforms (CD99 and CD99MIC2) due to alternative splicing, though their functional differences remain under investigation.
CD99 antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics. In pathology, they serve as key markers for identifying Ewing sarcoma and peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNETs), which overexpress CD99 due to *MIC2* gene involvement. They also aid in distinguishing T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma from other malignancies. In research, CD99 antibodies help elucidate mechanisms in immune regulation, cancer metastasis, and inflammatory diseases. Recent studies explore its role in modulating ERK and AKT signaling pathways, as well as its potential as a therapeutic target. However, nonspecific binding remains a challenge, requiring careful validation in experimental and clinical settings.
Overall, CD99 antibodies remain vital tools for understanding cell biology and improving diagnostic precision in oncology and immunology.
×