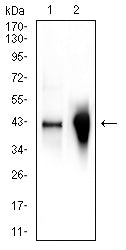
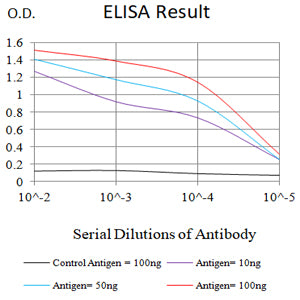
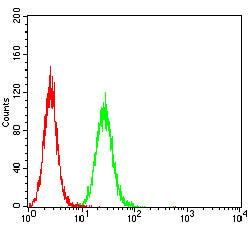
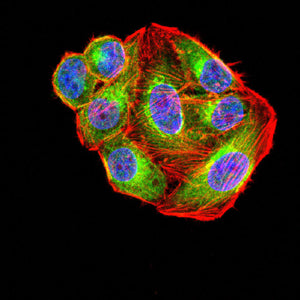
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GS; GLNS; PIG43; PIG59 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2752 |
| clone | 2D11A2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human GLUL (AA: 2-121) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于GLUL(谷氨酰胺合成酶)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Glutamine synthetase: localization in astrocytes"*
**作者**: Martinez-Hernandez A, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组织化学技术,利用GLUL抗体揭示了谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)在哺乳动物中枢神经系统中的特异性分布,证实其在星形胶质细胞中高表达,支持其在谷氨酸-谷氨酰胺循环中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *"Hepatic glutamine synthetase controls NASH-induced oxidative stress via ameliorating lipid peroxidation"*
**作者**: Tanizawa Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过GLUL抗体检测肝脏谷氨酰胺合成酶表达,发现其在非酒精性脂肪性肝炎(NASH)中通过调节谷胱甘肽合成减轻脂质过氧化,提出GS可能成为代谢相关肝病的治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *"Glutamine synthetase activity fuels the proliferation of glioblastoma cells"*
**作者**: Rosati A, et al.
**摘要**: 利用GLUL抗体分析神经胶质瘤细胞系,发现谷氨酰胺合成酶通过维持细胞内谷氨酰胺水平促进肿瘤细胞增殖,提示抑制GS可能作为胶质母细胞瘤的潜在治疗策略。
---
以上研究均涉及GLUL抗体的应用,涵盖神经生物学、肝病代谢及肿瘤学领域,展示了该抗体在基础与临床研究中的重要性。
**Background of GLUL Antibody**
GLUL (glutamine synthetase) is a key enzyme encoded by the *GLUL* gene, responsible for catalyzing the ATP-dependent conversion of glutamate and ammonia into glutamine. This reaction is critical for nitrogen metabolism, neurotransmitter recycling, and maintaining cellular homeostasis. GLUL is highly expressed in the liver, brain (particularly in astrocytes), and kidneys, reflecting its role in detoxifying ammonia, supporting energy production, and modulating redox balance.
Antibodies targeting GLUL are widely used in research to study its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. In the central nervous system, GLUL is essential for the glutamate-glutamine cycle, which regulates excitatory neurotransmission. Dysregulation of GLUL has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), hepatic encephalopathy, and cancer, where altered glutamine metabolism supports tumor growth.
GLUL antibodies are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate tissue-specific expression patterns or changes under disease conditions. For example, in liver disease models, reduced GLUL levels may indicate impaired detoxification, while in gliomas, elevated expression correlates with aggressive tumor behavior.
Validation of GLUL antibodies is crucial, requiring specificity checks via knockout controls or siRNA-mediated silencing. Commercial antibodies often target conserved regions, such as the N-terminal domain, to ensure cross-reactivity in multiple species. As glutamine metabolism gains attention in therapeutic research, GLUL antibodies remain vital tools for unraveling metabolic dysregulation and identifying biomarkers or therapeutic targets.
×