
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
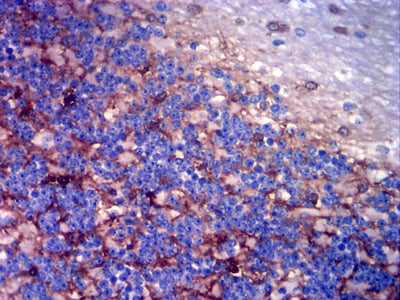
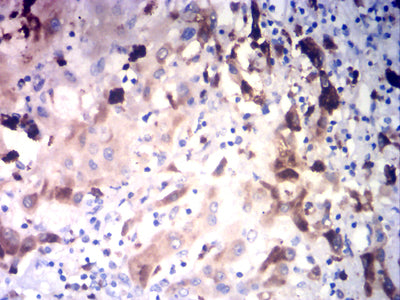
| IHC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
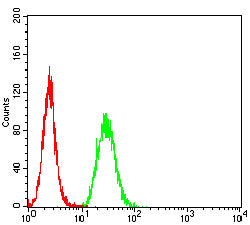
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
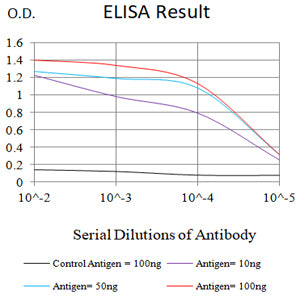
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GS; GLNS; PIG43; PIG59 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2752 |
| clone | 5A3B4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human GLUL (AA: 2-121) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于GLUL(谷氨酰胺合成酶)抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **"Astrocytic Glutamine Synthetase: Importance in Ammonia Homeostasis"**
- **作者**: Bak LK, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2012)
- **摘要**: 该研究通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,使用GLUL抗体分析星形胶质细胞在不同培养密度下的谷氨酰胺合成酶表达变化,揭示其在氨代谢平衡中的调控作用。
2. **"Regulation of Glutamine Synthetase in Glioblastoma Cells by Autophagy"**
- **作者**: van der Vos KE, Coffer PJ (2016)
- **摘要**: 文章利用GLUL抗体探究胶质母细胞瘤中自噬对谷氨酰胺合成酶表达的影响,发现肿瘤细胞通过上调GLUL增强谷氨酰胺代谢以支持增殖。
3. **"Developmental Regulation of Glutamine Synthetase in Liver"**
- **作者**: Lie-Venema H, et al. (2003)
- **摘要**: 研究通过免疫组化结合GLUL抗体,比较胚胎期与成年小鼠肝脏中谷氨酰胺合成酶的分布差异,提示其在肝发育和代谢功能成熟中的关键作用。
4. **"Astrocyte Glutamine Synthetase Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease"**
- **作者**: Robinson MB, et al. (2014)
- **摘要**: 该文献通过GLUL抗体检测阿尔茨海默病模型中星形胶质细胞的谷氨酰胺合成酶活性下降,并探讨其与神经元兴奋性毒性损伤的关联。
这些研究展示了GLUL抗体在神经代谢、肿瘤生物学、发育及疾病机制研究中的广泛应用。
GLUL (glutamine synthetase) is a key enzyme in cellular nitrogen metabolism, catalyzing the ATP-dependent conversion of glutamate and ammonia to glutamine. This enzyme plays critical roles in maintaining nitrogen homeostasis, detoxifying ammonia in the brain, and supporting neurotransmitter recycling. GLUL is highly expressed in astrocytes within the central nervous system, where it contributes to the glutamate-glutamine cycle essential for neuronal function. It also functions in hepatic ammonia metabolism and tumor microenvironment regulation, with elevated GLUL activity observed in certain cancers to support rapid cell proliferation.
GLUL antibodies are vital tools for studying this enzyme's expression, localization, and function across biological contexts. They are widely used in neuroscience to investigate astrocyte biology and neurological disorders like hepatic encephalopathy. In cancer research, these antibodies help characterize metabolic adaptations in tumors. Common applications include immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence, with validation required for specific experimental models. As both a metabolic regulator and potential disease biomarker, GLUL remains a focus of therapeutic development, making its corresponding antibodies crucial for both basic research and clinical translation studies. Commercial GLUL antibodies are typically developed in rabbit or mouse hosts, targeting specific epitopes of human or model organism proteins.
×