| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
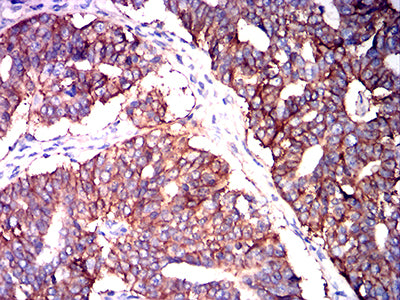
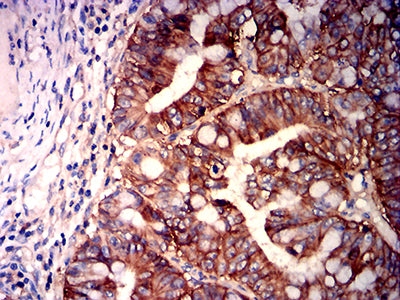
| IHC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
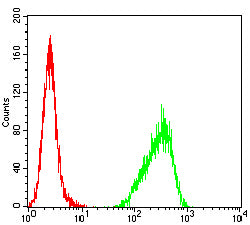
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
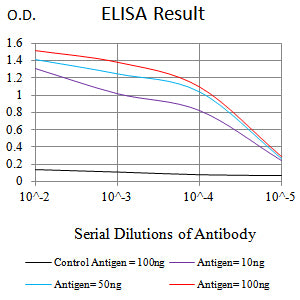
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BSG; OK; 5F7; TCSF; EMMPRIN |
| Entrez GeneID | 682 |
| clone | 2D8C11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD147 (AA: extra 138-323) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD147抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容:
1. **文献名称**:*CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to immune cells*
**作者**:Wang, K., et al.
**摘要**:该研究提出CD147是新冠病毒(SARS-CoV-2)感染免疫细胞的潜在受体,发现抗CD147抗体(如Meplazumab)可阻断病毒与宿主细胞的结合,为COVID-19治疗提供新靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD147 inhibits tumor progression and metastasis by blocking MMP activity in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**:Bougatef, F., et al.
**摘要**:研究证明抗CD147抗体通过抑制金属蛋白酶(MMPs)的活性,减少肝癌细胞侵袭和转移,揭示了CD147在肿瘤微环境调控中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD147 antibody suppresses inflammatory response in sepsis-induced acute lung injury by regulating glycolysis in neutrophils*
**作者**:Chen, Z., et al.
**摘要**:该文献发现抗CD147抗体通过调节中性粒细胞的糖酵解途径,减轻脓毒症相关急性肺损伤中的过度炎症反应,为免疫代谢干预提供新策略。
4. **文献名称**:*CD147 modulates autophagy and apoptosis in cancer-associated fibroblasts to promote tumor growth*
**作者**:Jiang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:研究显示抗CD147抗体可通过靶向肿瘤相关成纤维细胞(CAFs),抑制其自噬和促肿瘤功能,从而减缓肿瘤生长和血管生成。
以上文献涵盖了CD147抗体在病毒感染、肿瘤治疗及炎症调控中的机制与应用。
CD147. also known as Basigin or EMMPRIN (Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer), is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is widely expressed in various cell types, including immune cells, endothelial cells, and tumor cells. CD147 plays a pivotal role in regulating cell-cell interactions, inflammation, tissue remodeling, and tumor progression by promoting the production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and facilitating cellular adhesion. Its overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in cancers, infectious diseases (e.g., malaria, COVID-19), and inflammatory conditions.
CD147 antibodies are designed to target specific epitopes on this protein, aiming to block its pathological interactions. In oncology, these antibodies inhibit tumor growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis by disrupting CD147-mediated MMP activation and signaling pathways. Notably, CD147 has been implicated in SARS-CoV-2 entry, sparking interest in its antibodies as potential COVID-19 therapeutics. Structurally, CD147 contains two extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains, a transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail, making it accessible for antibody binding.
Current research focuses on developing monoclonal antibodies (e.g., Meplazumab) for clinical use, with ongoing trials in cancers and viral infections. Challenges include optimizing specificity to avoid off-target effects and overcoming resistance mechanisms. CD147 antibodies represent a promising yet complex therapeutic avenue, bridging immunology, oncology, and infectious disease research.
×