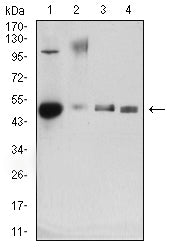
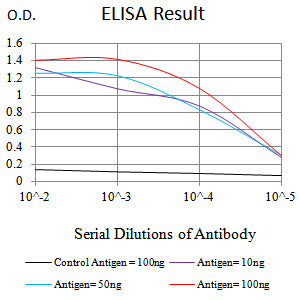
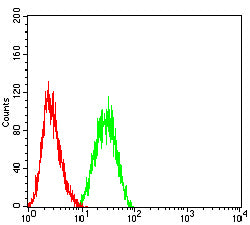
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Entrez GeneID | 947 |
| clone | 1D3H10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD34 (AA: extra 32-290) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD34抗体的3篇经典文献及其摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*CD34: structure, biology, and utility in diagnosis and therapy*
**作者**:Krause DS 等
**摘要**:综述CD34的分子结构、生物学功能及其在干细胞分离和临床诊断中的应用,强调CD34抗体在免疫分型和靶向治疗中的价值。
2. **文献名称**:*Purification and characterization of mouse hematopoietic stem cells*
**作者**:Spangrude GJ 等
**摘要**:利用CD34抗体结合其他表面标记分离小鼠造血干细胞,验证其自我更新和分化能力,奠定干细胞分离技术基础。
3. **文献名称**:*CD34 expression by murine hematopoietic stem cells mobilized by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor*
**作者**:Randall TD 等
**摘要**:研究G-CSF诱导的小鼠造血干细胞中CD34表达动态变化,揭示CD34抗体在干细胞动员及移植研究中的关键作用。
---
均为领域内高引文献,涵盖基础机制与临床应用。如需特定主题(如肿瘤诊断)的文献,可进一步补充说明。
CD34 is a transmembrane glycoprotein primarily expressed on the surface of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, vascular endothelial cells, and certain stromal cells. Discovered in the 1980s, it belongs to the sialomucin family and functions as a cell-cell adhesion molecule, though its exact biological role remains partially unclear. Structurally, CD34 contains a heavily glycosylated extracellular domain, a single transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail. Its expression is commonly associated with primitive cell populations, making it a key marker for identifying and isolating stem cells in research and clinical applications, such as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
CD34 antibodies, developed against specific epitopes of this protein, are widely used in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to characterize cell populations. In diagnostics, CD34 immunostaining aids in identifying vascular tumors (e.g., angiosarcoma) and distinguishing certain soft tissue neoplasms (e.g., gastrointestinal stromal tumors from dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans). However, its expression isn't lineage-specific, requiring careful interpretation alongside other markers.
While CD34's role in cell adhesion, migration, and differentiation signaling is studied in contexts like vascular repair and cancer metastasis, its functional mechanisms remain an active research area. Variations in antibody clones (e.g., QBEnd/10. Class II/III epitopes) may yield differing staining patterns, necessitating validation for specific applications.
×