| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
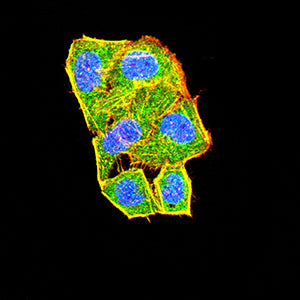
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/20 - 1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
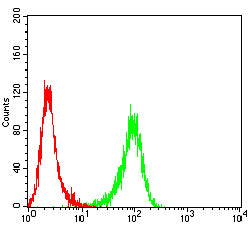
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
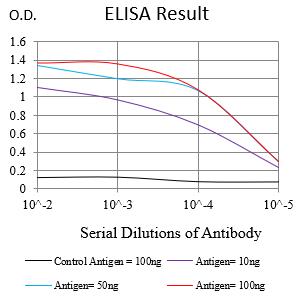
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p180; r150; CPAMD7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 135228 |
| clone | 1A3D3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 161.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD109 (AA: extra 1274-1421) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD109抗体的参考文献及简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**: *CD109 regulates tumor invasion and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer via TGF-β signaling*
**作者**: Zhang Y et al.
**摘要**: 本研究揭示CD109通过调控TGF-β/Smad信号通路,影响三阴性乳腺癌细胞的侵袭和转移能力。实验表明,CD109抗体可抑制肿瘤细胞上皮-间质转化(EMT)进程。
2. **文献名称**: *CD109 as a potential therapeutic target in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma*
**作者**: Hasegawa M et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现CD109在皮肤鳞状细胞癌中高表达,并与其预后不良相关。利用特异性CD109抗体阻断功能后,肿瘤细胞增殖和血管生成显著受抑制。
3. **文献名称**: *Monoclonal antibody targeting CD109 inhibits fibrosis in systemic sclerosis models*
**作者**: Li W et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种靶向CD109的单克隆抗体,并在系统性硬化症小鼠模型中验证其抗纤维化作用。机制研究表明,抗体通过阻断TGF-β1信号传导减轻组织纤维化。
4. **文献名称**: *CD109 modulates platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling in glioblastoma*
**作者**: Hu B et al.
**摘要**: 该研究证明CD109与胶质母细胞瘤中PDGFR信号通路相互作用,使用CD109抗体可增强肿瘤细胞对放疗的敏感性,提示其作为联合治疗靶点的潜力。
CD109 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the complement regulation protein family. Initially identified as a platelet antigen, it is expressed on activated T cells, endothelial cells, and subsets of stem or progenitor cells. CD109 interacts with TGF-β receptors, modulating TGF-β1 signaling pathways, and plays roles in cell proliferation, differentiation, and immune regulation. Its overexpression is observed in several cancers, including squamous cell carcinoma and glioblastoma, correlating with tumor progression and poor prognosis.
CD109 antibodies are essential tools for studying its biological functions and clinical relevance. They enable detection of CD109 expression in tissues/cells via techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blot. Specific monoclonal antibodies (e.g., clones TSP-1/18 or 109B4) target distinct extracellular epitopes, aiding in functional studies. Research using CD109 antibodies has revealed its dual role as both a tumor suppressor and promoter, depending on cellular context. Additionally, CD109 antibodies have diagnostic potential, as serum CD109 levels may serve as a biomarker for certain malignancies or inflammatory conditions. Recent studies also explore CD109's involvement in angiogenesis, fibrosis, and stem cell maintenance, highlighting its therapeutic targeting potential.
×