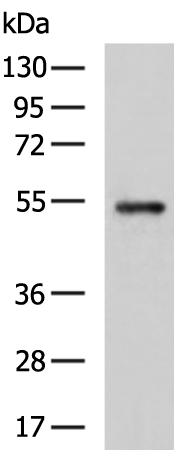
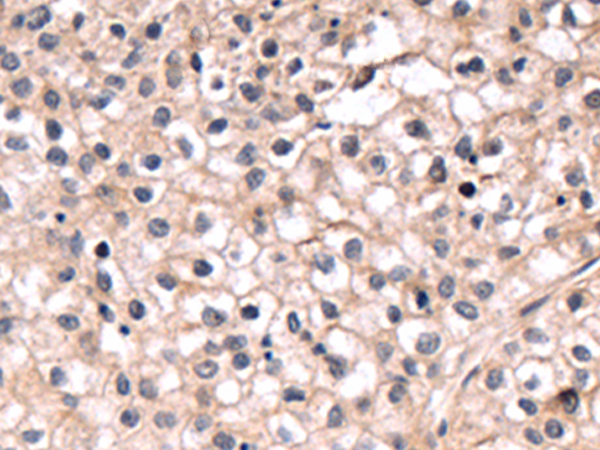
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AZ3B; C3AR; HNFAG09 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human C3AR1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于C3AR1抗体的3篇代表性文献及其简要摘要:
1. **标题**:*Molecular cloning and characterization of the human anaphylatoxin C3a receptor*
**作者**:Crass, T., Raffetseder, U., Martin, U., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次克隆并表征了人C3AR1受体,开发了特异性抗体用于检测其在多种免疫细胞中的表达,揭示了C3a-C3AR1信号在炎症反应中的调控机制。
2. **标题**:*A key role for the receptor for the complement C3a in the pathogenesis of asthma*
**作者**:Kohl, J., Baelder, R., Lewkowich, I.P., et al.
**摘要**:通过使用C3AR1阻断抗体,研究证实C3a-C3AR1通路在哮喘模型中促进嗜酸性粒细胞浸润和气道高反应性,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **标题**:*C3a receptor signaling in neurodegenerative disorders: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications*
**作者**:Woodruff, T.M., Ager, R.R., Tenner, A.J., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用C3AR1中和抗体,证明抑制C3a信号可减轻阿尔茨海默病模型中的神经炎症和神经元损伤,为神经退行性疾病提供新干预策略。
注:若需获取全文,建议通过PubMed或Sci-Hub输入标题/作者进一步检索。
C3aR1 (Complement C3a Receptor 1) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds to the complement component C3a, a potent anaphylatoxin generated during complement system activation. It plays a critical role in innate immunity, inflammation, and cell signaling. C3aR1 is expressed on immune cells (e.g., mast cells, eosinophils, macrophages), endothelial cells, and neurons, mediating pro-inflammatory responses, chemotaxis, and tissue repair. Dysregulation of C3a-C3aR1 signaling is implicated in autoimmune diseases (e.g., asthma, rheumatoid arthritis), neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s), and cancer progression.
C3aR1-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying receptor localization, expression levels, and functional interactions. They enable researchers to block or modulate C3aR1 activity in vitro and in vivo, helping to dissect its role in disease mechanisms. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against C3aR1 are often developed for therapeutic exploration, particularly in inflammatory and immune-mediated conditions. Additionally, these antibodies are used in techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting to validate C3aR1 presence in experimental models. Recent studies highlight C3aR1's potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target, especially in cancer immunotherapy, where its inhibition may suppress tumor-associated inflammation and immune evasion. However, challenges remain in achieving tissue-specific targeting due to the receptor's broad expression.
×