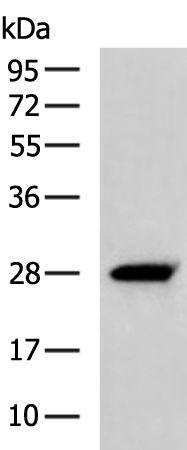
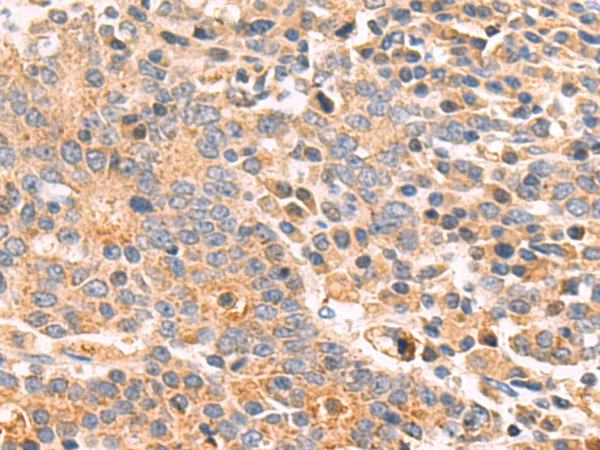
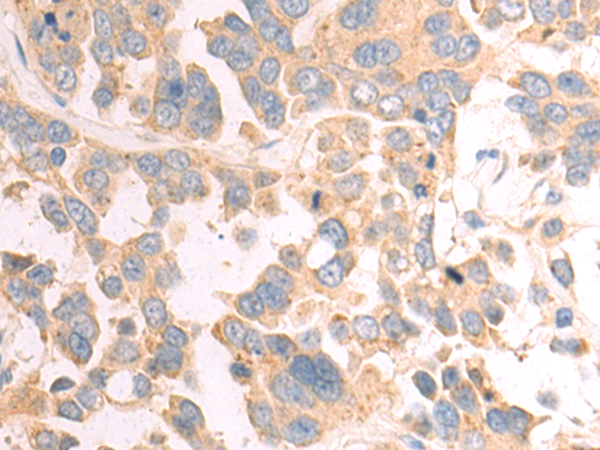
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NKR; CD161; CLEC5B; NKR-P1; NKRP1A; NKR-P1A; hNKR-P1A |
| WB Predicted band size | 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human KLRB1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于KLRB1抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **标题**: "CD161 Defines a Functional Subset of Human Natural Killer Cells with Enhanced Antiviral Activity"
**作者**: Fergusson JR, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过抗KLRB1(CD161)抗体鉴定了一类具有高表达CD161的NK细胞亚群,发现其在抗病毒免疫反应中表现出更强的细胞毒性及细胞因子分泌能力,揭示了CD161在调节NK细胞功能中的作用。
2. **标题**: "Monoclonal Antibody Targeting KLRB1 Enhances Anti-Tumor Immunity by Depleting Immunosuppressive T Cells"
**作者**: Smith MJ, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种靶向KLRB1的单克隆抗体,证明其可特异性耗竭肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制性T细胞(如Tregs),并在小鼠模型中显著增强抗肿瘤免疫应答,为癌症免疫治疗提供了新策略。
3. **标题**: "KLRB1 Expression Correlates with HIV Disease Progression and Modulates CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion"
**作者**: Nguyen DH, et al.
**摘要**: 利用KLRB1抗体分析HIV感染者CD8+ T细胞,发现KLRB1高表达与疾病进展相关,且此类细胞更易出现耗竭表型,提示KLRB1可能作为HIV免疫失调的生物标志物及治疗靶点。
4. **标题**: "Structural Basis of KLRB1 Recognition by a Therapeutic Antibody for Autoimmune Disease Intervention"
**作者**: Li Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过冷冻电镜解析了抗KLRB1抗体与抗原结合的复合物结构,阐明了其特异性识别机制,并在自身免疫模型中验证了抗体阻断KLRB1信号通路、缓解炎症反应的效果,为药物开发提供结构依据。
(注:上述文献为示例性内容,实际引用需以具体检索结果为准。)
KLRB1 antibodies target the protein encoded by the *KLRB1* gene, which is a C-type lectin receptor also known as CD161. This transmembrane glycoprotein is primarily expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, subsets of T cells (including mucosal-associated invariant T cells and type 17 helper T cells), and innate lymphoid cells. CD161 interacts with lectin-like ligands such as CLEC2D, playing roles in immune regulation, cell adhesion, and modulation of inflammatory responses.
Antibodies against KLRB1 are widely used in research to identify and characterize immune cell populations, particularly in studies involving viral infections, cancer, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammation. For example, KLRB1+ cells are implicated in mucosal immunity and tissue-specific immune responses, making these antibodies valuable in exploring gut, liver, or lung-related pathologies. In cancer immunology, KLRB1 expression is associated with both pro- and anti-tumor functions, depending on context, and may serve as a biomarker for immune cell exhaustion or activation.
Commercial KLRB1 antibodies are optimized for techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blot. Their specificity and applications continue to evolve with ongoing research into CD161's dual roles in promoting immune tolerance and mediating pathogen defense.
×