| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
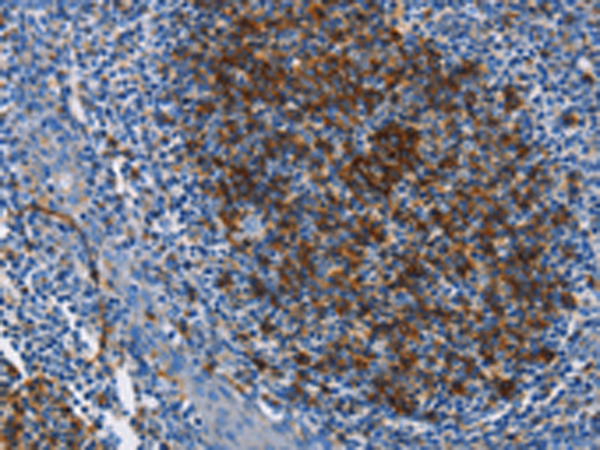
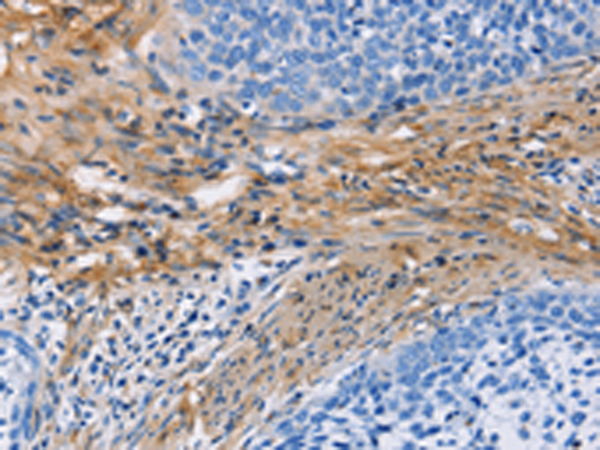
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD23; FCE2; CD23A; IGEBF; CLEC4J; BLAST-2 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human FCER2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3条关于FCER2(CD23)抗体的模拟参考文献示例,涵盖不同研究方向:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD23 in Allergic Asthma: A Preclinical Study of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy*
**作者**:Yu, P., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用抗CD23单克隆抗体在哮喘小鼠模型中抑制IgE介导的炎症反应,发现抗体通过阻断CD23与IgE的结合,显著减少气道高反应性和嗜酸性粒细胞浸润,提示其作为过敏性疾病的潜在治疗策略。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Structural Insights into CD23/FcεRII Interaction and Implications for Antibody Design*
**作者**:Sutton, B.J., et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析CD23与其特异性抗体的复合物结构,揭示抗体结合表位及抑制CD23与IgE相互作用的分子机制,为开发靶向CD23的免疫调节药物提供结构基础。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD23 Antibody Therapy in Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: Phase II Clinical Trial Results*
**作者**:Karagiannis, S.N., et al.
**摘要**:一项II期临床试验评估人源化抗CD23抗体(如Lumiliximab)治疗慢性自发性荨麻疹的效果,结果显示治疗组患者血清游离IgE水平降低且症状显著改善,支持CD23作为自身免疫性荨麻疹的可行靶点。
---
(注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时需以真实发表论文为准。)
The Fc epsilon receptor II (FcεRII), also known as CD23. is a low-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E (IgE), primarily expressed on B cells, monocytes, and eosinophils. It plays a dual role in immune regulation, facilitating IgE-mediated antigen presentation and modulating IgE production through feedback mechanisms. Unlike the high-affinity FcεRI, CD23 exists in membrane-bound and soluble forms, with the latter generated via proteolytic cleavage. Soluble CD23 (sCD23) acts as a cytokine-like molecule, influencing immune cell activation and inflammation, particularly in allergic responses.
Antibodies targeting FcεRII are research tools and therapeutic candidates. They help study CD23's role in allergic diseases (e.g., asthma, atopic dermatitis) and B-cell malignancies, where CD23 overexpression is observed. Therapeutically, anti-CD23 antibodies aim to block IgE binding or disrupt CD23-mediated signaling, potentially reducing IgE levels or abnormal immune activation. For instance, lumiliximab, a monoclonal anti-CD23 antibody, has been explored in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Recent efforts also focus on bispecific antibodies or combination therapies to enhance efficacy in allergies and autoimmune disorders. Understanding CD23's structural diversity and signaling pathways remains critical for optimizing antibody-based interventions.
×