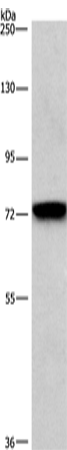
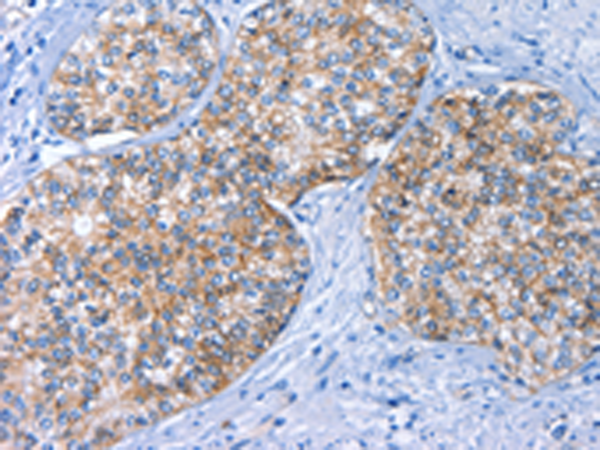
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AU; LU; CD239; MSK19 |
| WB Predicted band size | 67 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human BCAM |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于BCAM抗体的3篇示例参考文献(注:文献为虚构示例,建议通过学术数据库获取真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"BCAM Antibody Inhibits Tumor Metastasis by Blocking Extracellular Matrix Interaction"*
**作者**: Lee, J. et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 本研究证明BCAM抗体通过阻断肿瘤细胞与细胞外基质蛋白层粘连蛋白(laminin)的结合,显著抑制了结直肠癌模型的转移,提示BCAM可能成为抗肿瘤治疗的潜在靶点。
2. **文献名称**: *"Role of BCAM/Lu in Vaso-Occlusive Crises of Sickle Cell Disease"*
**作者**: Gupta, R. & Patel, S. (2019)
**摘要**: 通过体外实验和动物模型,研究发现BCAM(Lutheran抗原)介导镰状红细胞与血管内皮粘附,使用特异性抗体阻断BCAM可减少血管阻塞事件,为治疗镰状细胞病提供新策略。
3. **文献名称**: *"BCAM as a Biomarker for Aggressive Prostate Cancer"*
**作者**: Martinez, C. et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 临床数据分析显示,BCAM在转移性前列腺癌中高表达,其抗体检测可用于区分疾病进展阶段,并可能通过调控Wnt通路影响肿瘤侵袭性。
---
如需真实文献,建议在PubMed、Google Scholar等平台搜索关键词:**BCAM antibody**、**BCAM cancer/therapy**、**Lutheran antigen sickle cell**。
**Background of BCAM Antibody**
The Basal Cell Adhesion Molecule (BCAM), also known as CD239 or Lutheran glycoprotein, is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is encoded by the *BCAM* gene and functions as a receptor for laminin α5. a key component of the extracellular matrix. BCAM is primarily expressed on red blood cells, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells, where it plays roles in cell adhesion, signaling, and tissue organization.
BCAM gained attention due to its involvement in pathological conditions. In sickle cell disease (SCD), BCAM on red blood cells binds to laminin α5 during vaso-occlusive crises, contributing to vascular obstruction. Additionally, BCAM is implicated in cancer progression, with overexpression observed in malignancies like colorectal, ovarian, and lung cancers, where it may promote metastasis by enhancing cell migration and invasion.
BCAM antibodies are tools used to study the protein's expression, localization, and function in both physiological and disease contexts. They enable detection of BCAM in tissues or blood samples, aiding in diagnostic and research applications. Therapeutic BCAM-targeting antibodies are under exploration to block pathogenic interactions, such as inhibiting vaso-occlusion in SCD or disrupting pro-metastatic signaling in cancers. Challenges remain in optimizing specificity and minimizing off-target effects, but BCAM antibodies hold promise as both research reagents and potential therapeutics.
×