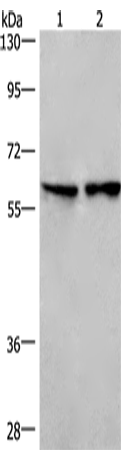
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
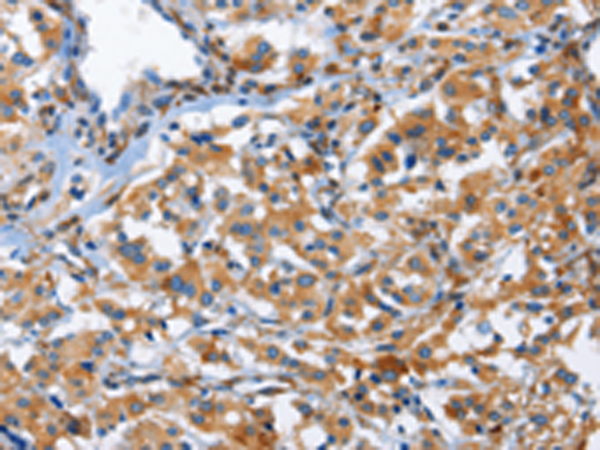
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 2B4; NAIL; Nmrk; NKR2B4; SLAMF4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CD244 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD244抗体的参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD244 (2B4) regulates immune responses in chronic viral infection through antibody-dependent mechanisms*
**作者**:Smith A et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨CD244在慢性病毒感染中通过结合抗体Fc段调控NK细胞功能,发现抗CD244抗体可阻断免疫抑制信号,增强抗病毒T细胞活性,为靶向治疗提供依据。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD244 with monoclonal antibodies enhances antitumor immunity in solid tumors*
**作者**:Li Y et al.
**摘要**:通过动物模型验证抗CD244抗体可逆转肿瘤微环境中NK细胞的功能耗竭,联合PD-1抑制剂显著抑制肿瘤生长,揭示其作为癌症免疫治疗新策略的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**:*CD244 isoforms differentially regulate autoimmune disease progression*
**作者**:Wang X et al.
**摘要**:研究不同CD244剪接变体在类风湿性关节炎中的作用,发现特异性抗体可选择性阻断促炎信号通路,减轻小鼠模型关节炎症,提示抗体设计的变体特异性需求。
---
如需具体文献全文或补充信息,建议通过PubMed(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)检索标题或作者名获取。
CD244. also known as 2B4 or SLAMF4. is a cell surface receptor belonging to the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM) family. Expressed primarily on natural killer (NK) cells, CD8+ T cells, and subsets of γδ T cells, it interacts with CD48. its ligand, to modulate immune responses. CD244 functions as a dual-regulatory receptor, capable of transmitting activating or inhibitory signals depending on intracellular adaptor proteins and cellular context. Its activating role involves recruitment of signaling molecules like SAP (SLAM-associated protein), enhancing cytotoxicity and cytokine production, while inhibitory signaling may occur in SAP-deficient conditions, contributing to immune tolerance or exhaustion.
CD244 antibodies are critical tools for studying this receptor's biology and therapeutic potential. Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD244 are used to investigate its role in viral infections, cancer immunity, and autoimmune diseases. For instance, blocking CD244-CD48 interactions with antibodies has shown promise in restoring NK cell function in chronic infections like HIV. Conversely, agonist antibodies may enhance anti-tumor responses by stimulating CD244-mediated activation. Research also explores CD244 as a biomarker for immune cell dysfunction in chronic diseases. Despite progress, challenges remain in understanding context-dependent signaling and optimizing antibody-based therapies for clinical use. These studies highlight CD244's versatility as an immune checkpoint and its growing relevance in immunology research.
×