| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
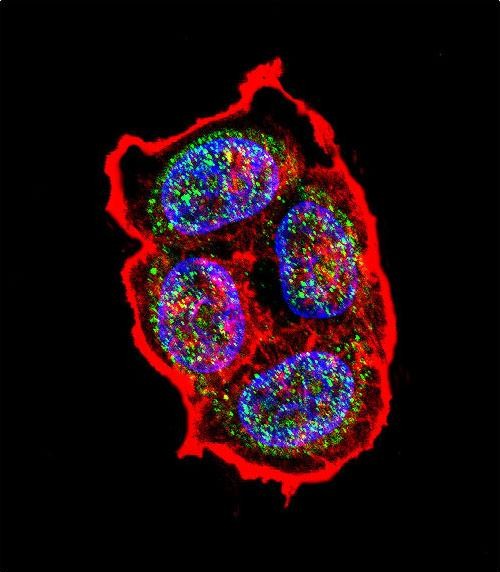
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
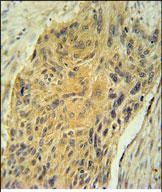
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Vasopressin-neurophysin 2-copeptin, AVP-NPII, Arg-vasopressin, Arginine-vasopressin, Neurophysin 2, Neurophysin-II, Copeptin, AVP, ARVP, VP |
| Entrez GeneID | 551 |
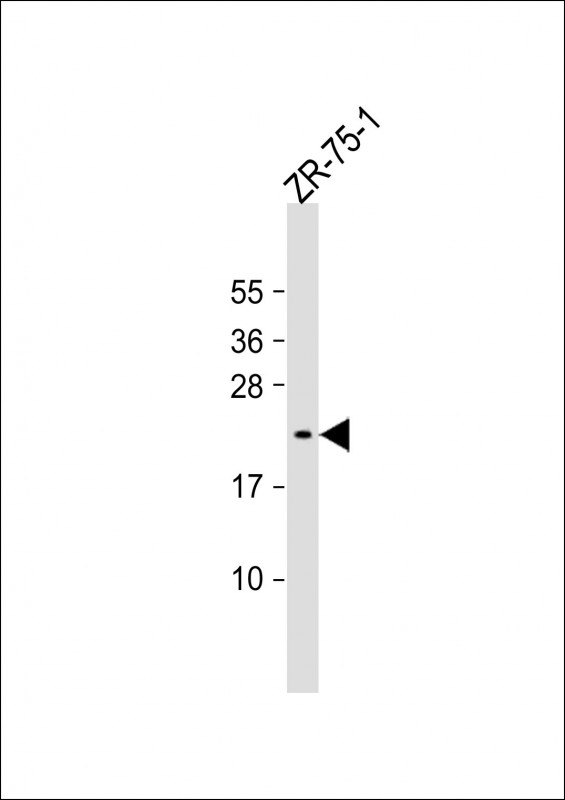
| WB Predicted band size | 17.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This AVP antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 102-129 amino acids of human AVP. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于BTLA抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
---
1. **标题**:*BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1*
**作者**:Watanabe N, et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次将BTLA鉴定为一种抑制性免疫检查点受体,发现其结构类似于CTLA-4和PD-1.并通过与HVEM结合抑制T细胞活化,为后续抗体开发奠定理论基础(发表于 *Nature Immunology*, 2003)。
---
2. **标题**:*Modulation of the CD8 T cell response to HSV-1 by the inhibitory receptor BTLA*
**作者**:Sedy JR, et al.
**摘要**:通过动物模型证明,阻断BTLA信号可增强CD8+ T细胞对单纯疱疹病毒(HSV-1)的免疫应答,提示BTLA抗体在增强抗病毒及抗肿瘤免疫中的潜力(发表于 *Journal of Clinical Investigation*, 2008)。
---
3. **标题**:*Icatolimab (anti-BTLA) in combination with toripalimab in advanced solid tumors: A phase Ib/II trial*
**作者**:Deng R, et al.
**摘要**:报道抗BTLA抗体(icatolimab)联合PD-1抑制剂的临床试验结果,显示在晚期实体瘤患者中具有可控的安全性及初步疗效,支持BTLA作为临床免疫治疗靶点(发表于 *Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer*, 2022)。
---
如需扩展,可补充早期机制研究(如Derré等关于BTLA在慢性病毒感染中的作用)或更多临床前/临床数据。
BTLA (B and T Lymphocyte Attenuator) is an inhibitory receptor belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, primarily expressed on immune cells like T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. Discovered in 2003. it plays a critical role in modulating immune responses to prevent excessive activation. Structurally, BTLA contains immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) that recruit phosphatases (e.g., SHP-1/2) to dampen signaling upon ligand binding. Its primary ligand, HVEM (Herpesvirus Entry Mediator), delivers co-inhibitory signals that suppress T-cell proliferation, cytokine production, and immune cell survival.
BTLA is implicated in immune tolerance, autoimmunity, and cancer. In autoimmune diseases, BTLA deficiency or dysfunction may contribute to hyperactive immunity, while in cancer, tumors exploit BTLA-mediated suppression to evade immune surveillance. Targeting BTLA with antibodies has emerged as a therapeutic strategy. Agonistic antibodies (enhancing BTLA signaling) are explored for treating autoimmune disorders, whereas antagonistic antibodies (blocking BTLA-HVEM interaction) aim to reinvigorate antitumor immunity, often in combination with PD-1/CTLA-4 inhibitors.
Preclinical studies show BTLA blockade enhances T-cell activity and synergizes with checkpoint inhibitors. Early-phase clinical trials are evaluating safety and efficacy in cancers like lymphoma and melanoma. Challenges include understanding context-dependent roles and optimizing therapeutic windows. BTLA antibodies represent a promising yet complex avenue for precision immunotherapy.
×