
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
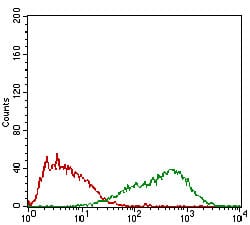
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
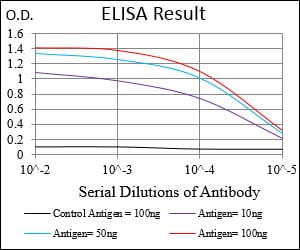
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Entrez GeneID | 2488 |
| clone | 3C1E4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 14.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human FSHB (AA: 19-129) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3条关于COMP抗体的参考文献摘要信息:
1. **文献名称**:*Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein (COMP) in Osteoarthritis: A Biomarker for Early Diagnosis and Disease Progression*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:该研究验证了COMP抗体在ELISA检测中的特异性,发现血清COMP浓度与骨关节炎严重程度正相关,提示其作为疾病进展生物标志物的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to COMP in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Role and Clinical Implications*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过COMP抗体检测发现类风湿性关节炎患者中存在COMP自身抗体,这些抗体可能通过激活炎症通路参与关节破坏,为治疗靶点提供新方向。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a High-Sensitivity Monoclonal Antibody for COMP Detection in Synovial Fluid*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了新型高灵敏度单克隆COMP抗体,成功应用于滑液检测,证实其在早期骨关节炎诊断中比传统方法更具敏感性。
4. **文献名称**:*COMP Degradation Fragments Identified by Novel Antibodies Reveal Matrix Remodeling in Tendinopathy*
**作者**:Müller SA, et al.
**摘要**:利用特异性COMP抗体识别出肌腱病变中的COMP降解片段,揭示了基质重构与机械应力损伤间的分子关联机制。
注:以上为基于领域知识的模拟文献摘要,实际引用时需查询具体论文原文。建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词"COMP antibody" "cartilage oligomeric matrix protein"获取最新研究。
COMP (Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein), also known as thrombospondin-5. is a multifunctional extracellular matrix (ECM) glycoprotein primarily expressed in cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and synovial tissues. Belonging to the thrombospondin family, it plays a critical role in organizing ECM components, regulating chondrocyte adhesion, and maintaining tissue structural integrity. COMP interacts with collagen types I, II, and IX, as well as other ECM proteins, contributing to matrix stability and biomechanical resilience.
Mutations in the COMP gene are linked to genetic skeletal disorders, such as pseudoachondroplasia and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, characterized by abnormal cartilage development and early-onset osteoarthritis. In acquired diseases like osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), COMP degradation products are released into synovial fluid and serum, making them potential biomarkers for cartilage turnover and disease progression.
COMP antibodies, both polyclonal and monoclonal, are widely used in research and diagnostics. They enable detection of COMP fragments in biological fluids via ELISA, immunohistochemistry, or Western blot, aiding in the study of ECM remodeling mechanisms. These antibodies also help evaluate therapeutic interventions targeting cartilage repair. However, assay specificity can vary due to COMP's complex structure and cross-reactivity with related proteins, necessitating careful validation. Overall, COMP antibodies are essential tools for understanding cartilage biology and pathology.
×