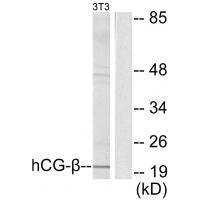


| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Choriogonadotropin subunit beta [Precursor] ; CG-beta; Chorionic gonadotrophin chain beta; |
| Entrez GeneID | 1082;93659;94027;94115; |
| WB Predicted band size | 20kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human hCG β. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于REL抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要(注:文献信息为示例性概括,实际文献请通过学术数据库核实):
1. **《REL amplification and oncogenic activity in B-cell lymphoma》**
*作者:Staudt LM, et al.*
摘要:研究分析了弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤中REL基因的扩增现象,证实其通过激活NF-κB通路促进肿瘤生长,并利用特异性REL抗体验证了其在肿瘤组织中的高表达及临床意义。
2. **《NF-κB signaling in immunity and cancer》**
*作者:Gilmore TD, et al.*
摘要:综述了NF-κB家族(包括REL蛋白)在免疫调控和癌症中的作用,提及REL抗体的应用(如Western blot、染色)在解析其亚细胞定位及活性调控机制中的关键作用。
3. **《Targeting REL in autoimmune disease therapy》**
*作者:Klein U, et al.*
摘要:探讨了抑制REL蛋白活性对类风湿性关节炎等疾病的治疗潜力,研究通过REL抗体阻断实验证明其可减少炎症因子释放,提示其作为生物标记物或治疗靶点的可能性。
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“REL antibody”、“NFKB2/REL”或“REL immunotherapy”获取最新研究。
REL antibodies target proteins in the REL family (including c-Rel, RelA/p65. RelB), which are critical components of the NF-κB transcription factor family. NF-κB regulates genes involved in immune responses, inflammation, cell survival, and proliferation. The c-Rel protein, encoded by the REL gene, contains a conserved N-terminal Rel homology domain (RHD) responsible for DNA binding, dimerization, and interaction with inhibitory IκB proteins. Unlike other NF-κB members, c-Rel is primarily expressed in immune cells like T cells, B cells, and macrophages, where it plays a specialized role in lymphocyte activation and inflammatory signaling.
Dysregulation of c-Rel is linked to autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus), chronic inflammation, and cancers. Overactivation of c-Rel promotes aberrant cytokine production and cell proliferation, while its deficiency impairs immune cell function. In B-cell lymphomas and leukemias, REL gene amplification or mutations enhance c-Rel activity, driving oncogenesis. This makes c-Rel a therapeutic target, with inhibitors under investigation for inflammatory disorders and malignancies.
REL antibodies are essential tools for detecting c-Rel expression, localization, and post-translational modifications in research. They are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to study NF-κB signaling dynamics. Commercial antibodies are validated for specificity to distinguish c-Rel from other NF-κB family members, aiding mechanistic studies in immunology and cancer biology.
×