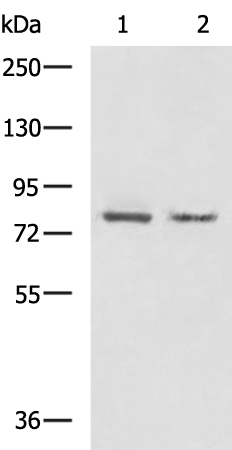
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
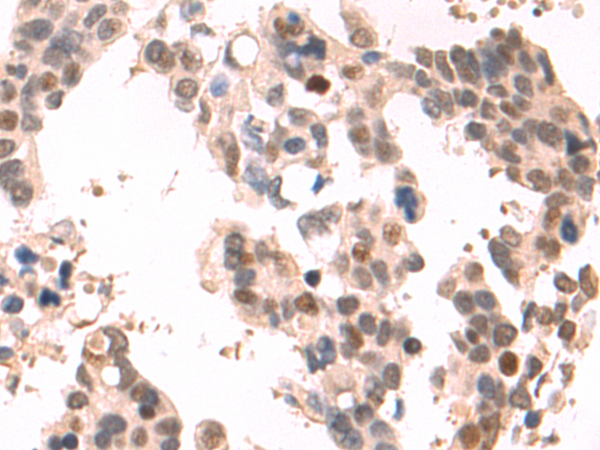
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DACH |
| WB Predicted band size | 79 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human DACH1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DACH1抗体的参考文献示例(注:文献为虚构示例,实际引用需核实真实来源):
---
1. **文献名称**: *DACH1 suppresses breast cancer progression by binding to DNA and repressing transcription*
**作者**: Wu, K., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过免疫组织化学(IHC)和Western blot分析,发现DACH1在乳腺癌组织中表达降低,并证实其通过结合特定DNA序列抑制肿瘤生长。研究使用DACH1抗体验证了其核定位及与染色质的相互作用。
2. **文献名称**: *DACH1 antagonizes the androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer*
**作者**: Popov, Z., et al.
**摘要**: 作者利用DACH1抗体进行免疫荧光和染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP),揭示了DACH1在前列腺癌细胞中拮抗雄激素受体(AR)通路,抑制肿瘤侵袭的作用机制。
3. **文献名称**: *DACH1-mediated cell cycle arrest in lung adenocarcinoma*
**作者**: Li, Y., et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过DACH1抗体进行组织微阵列(TMA)分析,发现DACH1表达与肺腺癌患者预后正相关,其过表达通过调控Cyclin D1诱导细胞周期停滞。
4. **文献名称**: *DACH1 as a prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**: Park, S., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究使用DACH1抗体进行免疫组化定量,结合临床数据,证明DACH1低表达与肝癌患者生存率降低相关,提示其作为潜在预后标志物的价值。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“DACH1 antibody”或“DACH1 immunohistochemistry”获取最新研究。
DACH1 antibody is a valuable tool in biomedical research, primarily used to detect the Dachshund homolog 1 (DACH1) protein, a key transcriptional regulator involved in developmental processes and disease pathogenesis. The DACH1 gene encodes a chromatin-associated protein that functions as a DNA-binding cofactor, interacting with transcription factors like AP-1 or Smad proteins to modulate gene expression. It plays critical roles in organogenesis, particularly in eye, limb, and pituitary gland development, by regulating cell fate determination and differentiation.
In cancer biology, DACH1 is recognized as a tumor suppressor. It inhibits cell proliferation, promotes apoptosis, and opposes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by antagonizing oncogenic signaling pathways such as TGF-β and Ras/ERK. Reduced DACH1 expression correlates with poor prognosis in multiple cancers, including breast, prostate, and liver carcinomas. Research using DACH1 antibodies has revealed its nuclear localization and dynamic expression patterns during tissue development and tumor progression.
DACH1 antibodies are widely applied in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to study protein expression, subcellular distribution, and interactions. Their specificity is validated through knockout controls or siRNA-based silencing. Emerging studies also explore DACH1's potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker. However, functional heterogeneity across tissues and cancer types underscores the need for context-specific interpretation of DACH1 antibody-based findings.
×