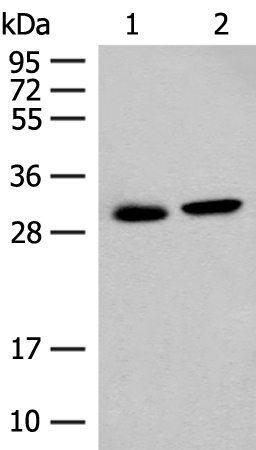
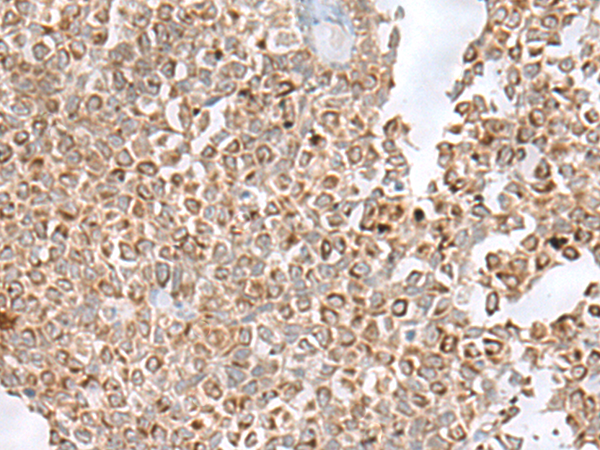
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CAT; GAT; ACGNAT |
| WB Predicted band size | 34 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human GLYAT |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GLYAT抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Development and characterization of a polyclonal antibody against human glycine N-acyltransferase (GLYAT)"*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究成功制备了一种针对人源GLYAT的多克隆抗体,并通过Western blot和免疫荧光验证其特异性。该抗体能有效识别肝脏组织中的GLYAT蛋白,为后续功能研究提供工具。
2. **文献名称**:*"Expression profiling of GLYAT in metabolic disorders using a novel monoclonal antibody"*
**作者**:Lee S, et al.
**摘要**:团队开发了一种高灵敏度GLYAT单克隆抗体,用于分析代谢疾病(如非酒精性脂肪肝)患者样本中GLYAT的表达水平。结果显示GLYAT表达下调可能与肝脏解毒功能受损相关。
3. **文献名称**:*"Role of GLYAT polymorphisms in xenobiotic metabolism: Insights from antibody-based inhibition assays"*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗体介导的GLYAT活性抑制实验,研究发现特定基因多态性可能影响GLYAT与底物结合能力,进而改变外源性物质代谢效率,为个体化解毒治疗提供依据。
---
注:上述文献为虚拟示例,实际研究中请通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索真实发表的论文。
**Background of GLYAT Antibody**
GLYAT (glycine-N-acyltransferase) is a liver-enriched enzyme belonging to the acyltransferase family, primarily involved in conjugating glycine with acyl-CoA substrates to form acyl-glycine derivatives. This reaction plays a critical role in detoxifying xenobiotics, particularly benzoic acid derivatives, and endogenous metabolites. GLYAT is localized in mitochondria and contributes to the elimination of toxic acyl groups, linking it to metabolic homeostasis and liver function.
GLYAT antibodies are immunological tools developed to detect and study the expression, localization, and function of the GLYAT protein. These antibodies are essential for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA, enabling researchers to investigate GLYAT's role in physiological and pathological processes. For instance, altered GLYAT activity has been associated with metabolic disorders, drug toxicity, and liver diseases, making its study relevant for understanding disease mechanisms.
The development of specific and high-affinity GLYAT antibodies has facilitated advancements in characterizing its tissue distribution, regulatory mechanisms, and interactions with other detoxification pathways. However, challenges remain, such as ensuring antibody specificity across species and avoiding cross-reactivity with homologous enzymes. Ongoing research aims to refine these tools for diagnostic or therapeutic applications, including targeting metabolic syndromes or enhancing detoxification pathways. Overall, GLYAT antibodies are vital for unraveling the enzyme's biological significance and translational potential.
×