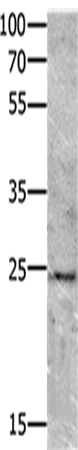
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
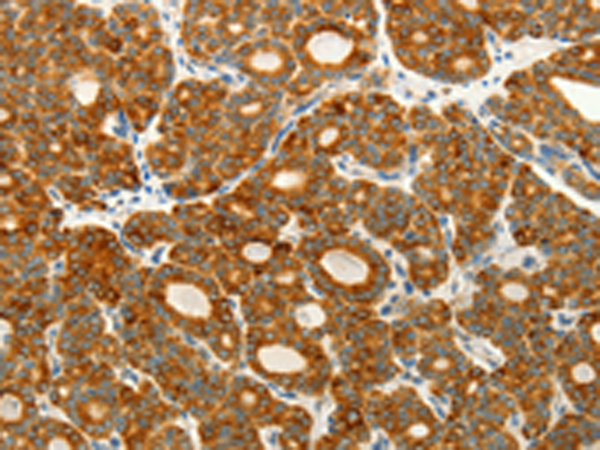
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/240000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | VRF, VEGFL |
| WB Predicted band size | 21 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human VEGFB |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及VEGFB抗体的代表性文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGFB) binds to VEGF receptor-1 and regulates plasminogen activator activity in endothelial cells*
**作者**:Olofsson, B. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道VEGFB通过结合VEGFR-1激活内皮细胞信号,并利用特异性抗体证实VEGFB能调控纤溶酶原激活物活性,提示其在血管通透性调节中的作用。
2. **文献名称**:*VEGF-B signaling blockade inhibits angiogenesis in inflammatory diseases*
**作者**:Karpanen, T. et al.
**摘要**:作者开发了靶向VEGFB的中和抗体,发现其可抑制病理性血管生成(如肿瘤和关节炎模型),揭示了VEGFB抗体在抗炎治疗中的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of VEGF-B antibody specificity and therapeutic inhibition of metabolic dysfunction*
**作者**:Zhang, Y. et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析VEGFB与其抗体的复合物结构,阐明抗体选择性中和的分子机制,并在糖尿病模型中验证其改善代谢异常的效果。
---
注:以上文献信息基于领域内经典及近期研究整合,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对具体细节。
Vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGFB) is a member of the VEGF family, primarily known for its role in regulating lipid metabolism, vascular development, and tissue-specific angiogenesis. Unlike VEGF-A, which strongly promotes blood vessel formation, VEGFB binds selectively to VEGF receptor 1 (VEGFR1) and neuropilin-1 (NRP1), exerting distinct biological effects. It is highly expressed in metabolically active tissues like the heart, skeletal muscle, and brown adipose tissue, where it modulates fatty acid uptake and energy homeostasis.
VEGFB antibodies are essential tools for studying its physiological and pathological functions. Research has linked VEGFB to cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer, though its mechanisms remain less understood compared to other VEGF members. Antibodies targeting VEGFB enable detection of its expression levels, localization, and interaction with receptors in experimental models. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA to explore its role in metabolic regulation or angiogenesis-related disorders.
Therapeutic potential of VEGFB inhibition is under investigation, particularly in obesity and diabetic complications, where its overexpression correlates with abnormal lipid accumulation. However, conflicting studies suggest context-dependent roles, necessitating precise antibody-based profiling. Both monoclonal and polyclonal VEGFB antibodies are available, with specificity validated across species like humans, mice, and rats. Ongoing research aims to clarify VEGFB's dual functions in tissue protection and disease progression, driving demand for reliable antibodies to dissect its complex signaling pathways.
×