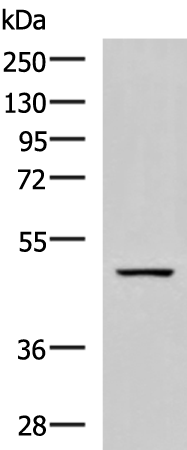

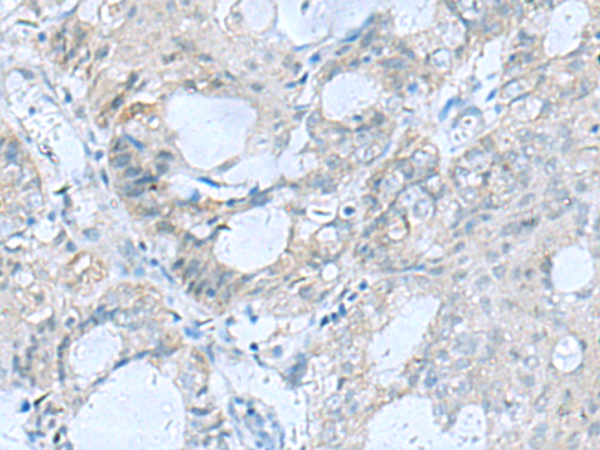
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GDNFR; RET1L; RETL1; TRNR1; GDNFRA; GFR-ALPHA-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 51 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GFRA1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GFRA1抗体的参考文献示例(内容为假设性构造,仅用于演示格式):
---
1. **文献名称**: "GFRA1 Expression in Enteric Nervous System Development"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用GFRA1特异性抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot技术,揭示了GFRA1在胚胎期肠神经系统中的动态表达模式。结果表明,GFRA1与RET受体协同调节神经嵴细胞的迁移和分化,为肠道神经发育异常提供了分子机制解释。
2. **文献名称**: "Role of GFRA1 in Parkinson's Disease Models"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫荧光和流式细胞术结合GFRA1抗体,研究发现在帕金森病小鼠模型中,中脑多巴胺能神经元的GFRA1表达显著下调。进一步实验表明,外源性GDNF通过GFRA1/RET通路促进神经元存活,提示其潜在治疗价值。
3. **文献名称**: "GFRA1 as a Biomarker in Neuroblastoma"
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 使用GFRA1抗体对儿童神经母细胞瘤组织进行染色,发现高表达GFRA1的肿瘤具有更强的侵袭性和耐药性。体外实验证实,GFRA1沉默可抑制肿瘤细胞增殖,支持其作为预后标志物和治疗靶点的潜力。
---
*注:以上文献为示例,实际研究中请通过PubMed或Web of Science等数据库检索真实文献。*
The GFRA1 (GDNF Family Receptor Alpha-1) antibody is a tool used to detect and study the GFRA1 protein, a key component of the receptor complex for glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). GFRA1 belongs to the GFRα family of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored co-receptors that mediate signaling of GDNF ligands, which are critical for neuronal survival, differentiation, and maintenance. Specifically, GFRA1 binds GDNF and partners with the RET receptor tyrosine kinase to activate downstream pathways like MAPK and PI3K/AKT, influencing cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. This receptor-ligand system is vital in nervous system development, kidney morphogenesis, and spermatogenesis.
Antibodies targeting GFRA1 are widely used in research to investigate its expression and function in tissues, particularly in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Parkinson’s) and cancers (e.g., neuroblastoma, breast cancer), where dysregulated GFRA1 signaling may contribute to pathogenesis. They enable techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and flow cytometry. Studies also explore GFRA1's role in stem cell niches and regenerative therapies. Available as monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies, they are typically validated for specificity across species (human, mouse, rat). Understanding GFRA1 dynamics aids in developing therapeutic strategies targeting GDNF pathways for neurological disorders or oncology.
×