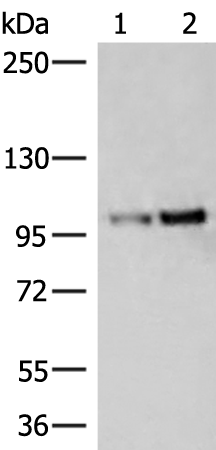


| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
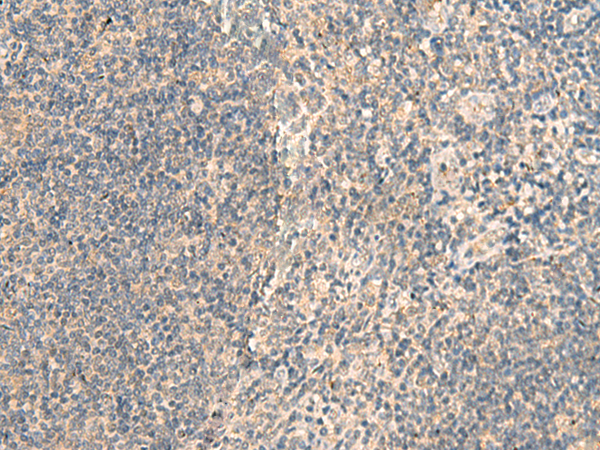
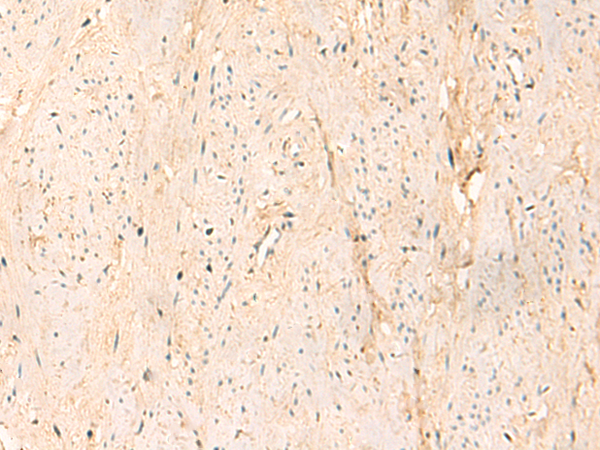
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GLUH1; GLUR1; GLURA; GluA1; HBGR1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 102 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GRIA1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇与GRIA1(GluA1)抗体相关的研究文献摘要简述:
1. **文献名称**:*AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity*
**作者**:Shepherd JD, Huganir RL
**摘要**:该综述讨论了AMPA受体(如GluA1/GRIA1)的转运机制及其在突触可塑性中的作用,其中提到使用特异性GRIA1抗体验证受体在神经元中的定位及表达变化。
2. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor GluA1 subunit regulates synaptic plasticity*
**作者**:Lee HK, Kameyama K, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过GRIA1磷酸化特异性抗体(如Ser831位点)揭示GluA1磷酸化对长时程增强(LTP)的调控,证实其在突触强度调节中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*GluA1 downregulation in Alzheimer's disease: an antibody-based proteomic analysis*
**作者**:Chang EH, Savage MJ, et al.
**摘要**:利用GRIA1抗体进行脑组织蛋白质组学分析,发现阿尔茨海默病患者海马区GluA1表达显著降低,提示其与认知衰退相关。
4. **文献名称**:*Antibody validation for specificity in Western blotting: a case study on anti-GluA1 antibodies*
**作者**:Herbert K, Collingridge GL
**摘要**:系统评估了多种市售GRIA1抗体的特异性,通过敲除模型验证抗体在Western blot和免疫组化中的可靠性,为实验选择提供依据。
(注:以上文献名为示例概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或期刊数据库检索具体标题及作者。)
The GRIA1 antibody targets the glutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA type subunit 1 (GluA1), a critical component of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors. These ligand-gated ion channels mediate the majority of fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. GluA1. encoded by the GRIA1 gene, forms tetrameric complexes with other AMPA receptor subunits (GluA2-4) to regulate synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. Its function is modulated by post-translational modifications, trafficking, and interactions with scaffolding proteins.
GRIA1 antibodies are widely used in neuroscience research to study GluA1 expression, localization, and dynamics in neuronal tissues. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding investigations into synaptic strength, long-term potentiation (LTP), and neurological disorders. Dysregulation of GluA1 has been implicated in conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, and schizophrenia, making these antibodies valuable for mechanistic and diagnostic studies. Specific GRIA1 antibodies are validated for species reactivity (e.g., human, mouse, rat) and application-specific performance. Researchers also utilize them to explore therapeutic targets, as AMPA receptor modulation holds potential for treating cognitive deficits and neurodegenerative diseases. Proper controls, including knockout validation, are essential to ensure antibody specificity given structural similarities among AMPA receptor subunits.
×