| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
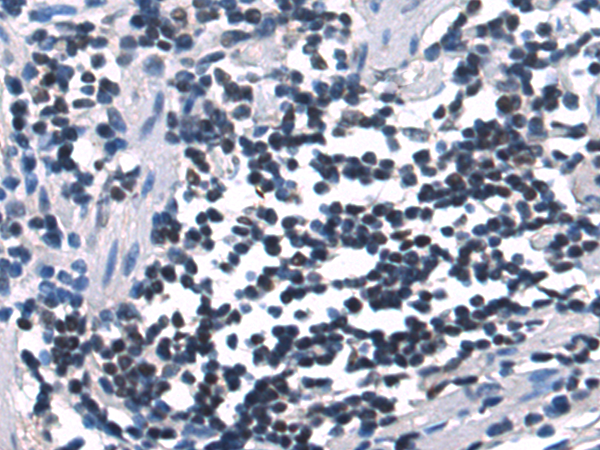
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CRCS3; MADH7; MADH8 |
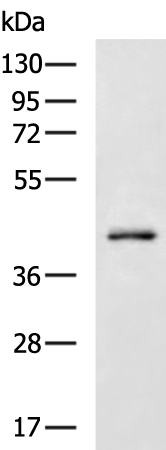
| WB Predicted band size | 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SMAD7 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SMAD7抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"SMAD7 expression in colorectal cancer cells predicts patient survival"*
**作者**:Monteiro et al.
**摘要**:研究利用SMAD7特异性抗体,通过免疫组化分析结直肠癌组织中SMAD7蛋白的表达水平,发现高表达SMAD7与患者不良预后相关,提示其可能通过抑制TGF-β信号促进肿瘤进展。
2. **文献名称**:*"Targeting SMAD7 with a specific antisense oligonucleotide enhances TGF-β signaling in experimental fibrosis"*
**作者**:Nakao et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种靶向SMAD7的反义寡核苷酸,并利用SMAD7抗体验证其在肝纤维化模型中的效果,结果显示抑制SMAD7可恢复TGF-β信号通路活性,减轻纤维化病变。
3. **文献名称**:*"SMAD7 knockdown by RNA interference reverses TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells"*
**作者**:Tojo et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术(使用SMAD7抗体)证明,抑制SMAD7表达可逆转乳腺癌细胞的上皮-间质转化(EMT),提示SMAD7是TGF-β促转移作用的关键调控因子。
(注:上述文献为示例,实际引用需根据具体研究核实作者及发表年份。)
SMAD7. a member of the inhibitory SMAD (I-SMAD) family, plays a critical role in regulating transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathways. As a key negative feedback regulator, SMAD7 binds to activated TGF-β or bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type I receptors, blocking the phosphorylation and activation of receptor-regulated SMADs (R-SMADs, e.g., SMAD2/3 or SMAD1/5/8). This interaction promotes receptor ubiquitination and degradation, effectively dampening downstream signaling. Dysregulation of SMAD7 has been implicated in various pathological conditions, including fibrosis, cancer, and inflammatory diseases, where its expression often correlates with disease progression or therapeutic resistance.
SMAD7 antibodies are essential tools for investigating these biological processes. They enable the detection and quantification of SMAD7 protein levels in experimental models and clinical samples through techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Researchers utilize these antibodies to study SMAD7's subcellular localization, protein-protein interactions, and post-translational modifications. Commercially available SMAD7 antibodies are typically developed in host species such as rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes within the protein's N-terminal or linker regions. Validation parameters include specificity checks via knockout controls and functional assays. Applications span mechanistic studies in TGF-β pathway modulation, drug development screening, and biomarker analysis in diseases like colorectal cancer, pancreatitis, and autoimmune disorders.
×