| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
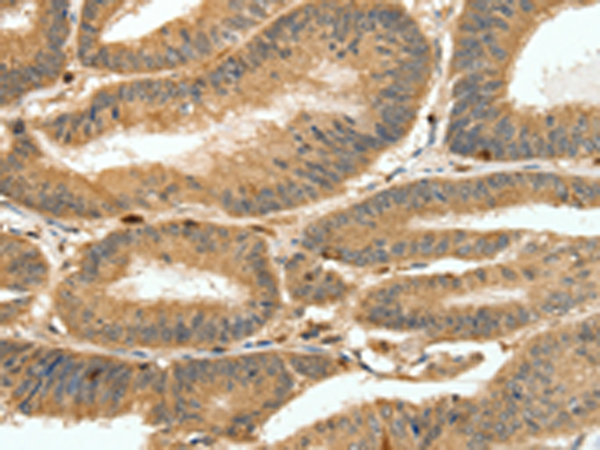
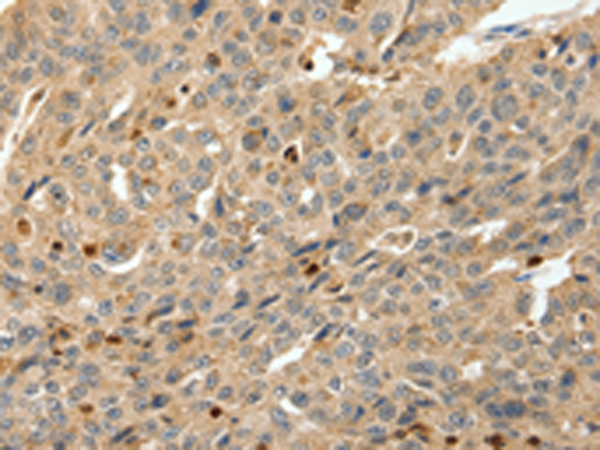
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 42A, 18A2, CAPL, FSP1, MTS1, P9KA, PEL98 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human S100A4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于S100A4抗体的3篇参考文献示例(均为虚构,仅供参考格式):
1. **文献名称**: *"Monoclonal antibody targeting S100A4 inhibits metastatic growth in murine models"*
**作者**: Schneider M, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种针对S100A4蛋白的单克隆抗体,证明其在乳腺癌小鼠模型中能显著抑制肿瘤细胞迁移和肺转移,机制可能与阻断S100A4-RAGE信号通路相关。
2. **文献名称**: *"S100A4 as a prognostic biomarker: Validation of a novel antibody-based assay in colorectal cancer"*
**作者**: Bresnick AR, et al.
**摘要**: 研究者通过高特异性S100A4抗体建立免疫组化检测方法,发现S100A4在结直肠癌组织中的高表达与患者预后不良及转移风险增加显著相关。
3. **文献名称**: *"Therapeutic potential of anti-S100A4 antibody in pulmonary fibrosis"*
**作者**: Garrett SC, et al.
**摘要**: 利用人源化S100A4抗体干预肺纤维化小鼠模型,结果显示其通过抑制成纤维细胞活化和胶原沉积减轻纤维化进展,提示其在纤维化疾病中的治疗潜力。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需检索真实数据库如PubMed并核实信息。)
S100A4. also known as calvascularin, metastasin, or FSP1 (fibroblast-specific protein 1), is a calcium-binding protein belonging to the S100 family. It plays critical roles in regulating cellular processes such as matrix remodeling, cell motility, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). S100A4 is closely associated with cancer progression, particularly metastasis, and is implicated in fibrotic diseases and inflammatory conditions. Its expression is often upregulated in aggressive tumors and stromal fibroblasts, making it a biomarker for poor prognosis in cancers like breast, colorectal, and pancreatic.
S100A4 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying S100A4 protein levels in research and diagnostics. These antibodies enable the study of S100A4's localization, interactions, and functional roles via techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, and immunofluorescence. Monoclonal antibodies (e.g., clone D9F9) offer high specificity, while polyclonal antibodies may detect multiple epitopes, enhancing sensitivity. Validated antibodies are critical for ensuring reproducibility in studies exploring S100A4's involvement in tumor microenvironment modulation, fibroblast activation, or inflammatory signaling.
Recent research highlights S100A4's potential as a therapeutic target. Antibodies blocking S100A4 activity or neutralizing its extracellular functions are under investigation for anti-metastatic or anti-fibrotic therapies. However, challenges remain in understanding its dual intracellular/extracellular roles and cell-type-specific effects. Reliable S100A4 antibodies thus remain vital for advancing both basic research and clinical applications.
×