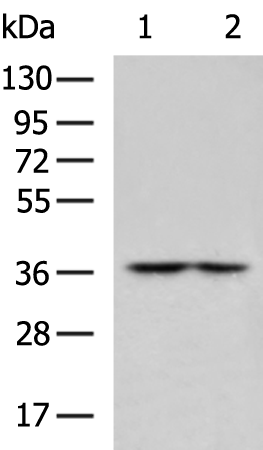
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EPM8; GDF1; LAG1; UOG1; GDF-1; LASS1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CERS1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CERS1抗体的3篇文献摘要信息(示例仅供参考,具体文献需根据实际检索补充):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Ceramide synthase 1 regulates peripheral nerve development and myelination in mice*
**作者**: Ginkel C, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用CERS1特异性抗体在小鼠模型中验证CERS1基因敲除后,外周神经鞘脂代谢异常及髓鞘形成缺陷,表明CERS1在神经发育中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *Tissue-specific expression of ceramide synthase 1 protein in mammalian systems*
**作者**: Pewzner-Jung Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化和Western blot分析,使用CERS1抗体证实其在哺乳动物脑组织及睾丸中高表达,提示其组织特异性功能可能与神经和生殖系统相关。
3. **文献名称**: *CERS1 deficiency alters hepatic lipid metabolism and promotes insulin resistance*
**作者**: Park JW, et al.
**摘要**: 研究采用CERS1抗体检测肝脏组织中CERS1蛋白水平,发现其缺失导致神经酰胺积累异常,进而加剧代谢紊乱和胰岛素抵抗。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Sci-Hub输入关键词“CERS1 antibody”或“ceramide synthase 1”检索最新研究。
**Background of CERS1 Antibody**
The CERS1 (ceramide synthase 1) antibody is a tool used to detect and study the CERS1 enzyme, a key player in sphingolipid metabolism. CERS1 belongs to the ceramide synthase family, which catalyzes the synthesis of ceramides—a class of lipid molecules critical for cell membrane structure, signaling, and apoptosis. Specifically, CERS1 is responsible for producing C18-ceramides by acylating sphinganine or sphingosine with a C18 fatty acid chain. This enzyme is highly expressed in the brain and peripheral tissues, implicating its role in neuronal function, myelination, and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
CERS1 antibodies are widely utilized in research to investigate tissue-specific expression patterns, subcellular localization, and regulatory mechanisms of CERS1. They enable techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding in the exploration of CERS1’s involvement in diseases. For instance, altered CERS1 activity has been linked to disrupted ceramide homeostasis in cancer, metabolic syndromes, and neurological conditions. These antibodies also help validate experimental models, such as CERS1-knockout mice, to dissect its physiological roles.
Despite their utility, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity due to homology among ceramide synthase isoforms. Ongoing studies aim to refine CERS1-targeting tools for therapeutic applications, including modulating ceramide levels to treat lipid metabolism-related disorders.
×