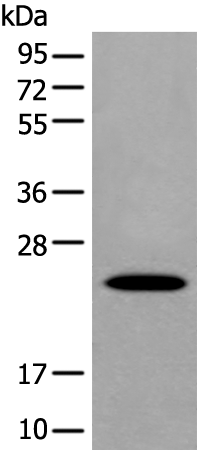
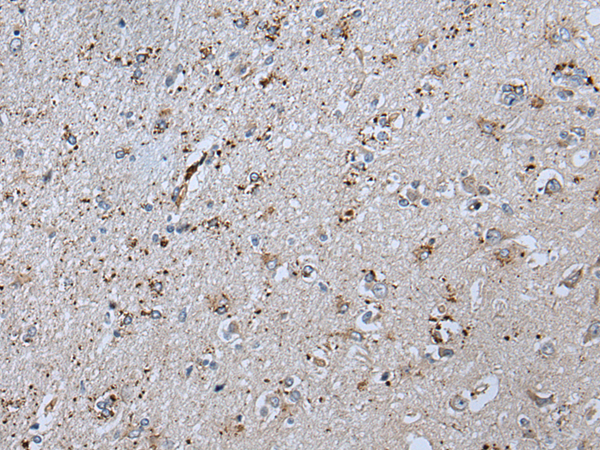
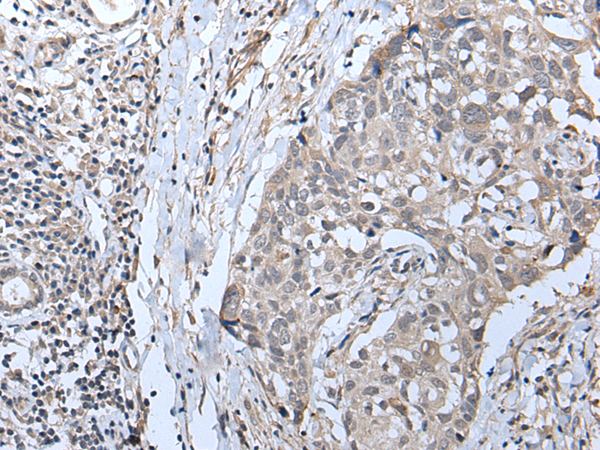
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 21 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human APOD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NEFH抗体的3篇文献摘要信息,供参考:
1. **文献名称**:Neurofilament heavy chain antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid as a biomarker of neurodegeneration
**作者**:Petzold A. et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了神经丝蛋白重链(NEFH)在脑脊液中的水平与神经退行性疾病(如肌萎缩侧索硬化症ALS)的关系,提出NEFH抗体检测可作为神经元损伤的生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:Axonal damage markers in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
**作者**:Brettschneider J. et al.
**摘要**:通过分析ALS患者的脑脊液样本,发现NEFH抗体水平显著升高,提示其与运动神经元轴突变性相关,可能用于疾病进展监测。
3. **文献名称**:Neurofilament proteins as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders
**作者**:Sjögren M. et al.
**摘要**:研究评估了NEFH与其他神经丝蛋白在阿尔茨海默病中的表达变化,发现其与tau蛋白异常聚集相关,可能反映神经轴突完整性丧失。
4. **文献名称**:Autoantibodies to neurofilament heavy chain in autoimmune encephalitis
**作者**:Wang Y. et al.
**摘要**:报道了在自身免疫性脑炎患者中检测到NEFH自身抗体,提示其可能参与针对神经元结构的免疫攻击机制。
注:以上文献信息为概括性示例,实际引用时需核对具体文献来源及内容准确性。
The neurofilament heavy polypeptide (NEFH), also known as NF-H, is a key component of neuronal intermediate filaments and a major structural protein in axons. It forms heteropolymers with neurofilament medium (NF-M) and light (NF-L) chains, contributing to the cytoskeletal architecture that maintains axonal caliber and facilitates intracellular transport. NEFH is characterized by its large molecular weight (≈200 kDa) and a carboxy-terminal tail domain rich in lysine-serine-proline (KSP) repeats, which undergo phosphorylation to regulate interactions with neighboring filaments and organelles.
Antibodies targeting NEFH are widely used in neuroscience research to study axonal integrity, degeneration, and regeneration. In pathological conditions such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer’s disease, and traumatic brain injury, NEFH expression or phosphorylation patterns are often altered, making it a biomarker for axonal damage. These antibodies enable the detection of NEFH in tissue samples (e.g., via immunohistochemistry) or bodily fluids (e.g., CSF, blood) using techniques like Western blot or ELISA. Specific antibodies may distinguish phosphorylated vs. non-phosphorylated forms, providing insights into disease mechanisms. Their applications extend to diagnostic tools, preclinical studies, and monitoring therapeutic responses in neurodegenerative disorders. However, variability in antibody specificity across species or phosphorylation states requires careful validation for experimental accuracy.
×