
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
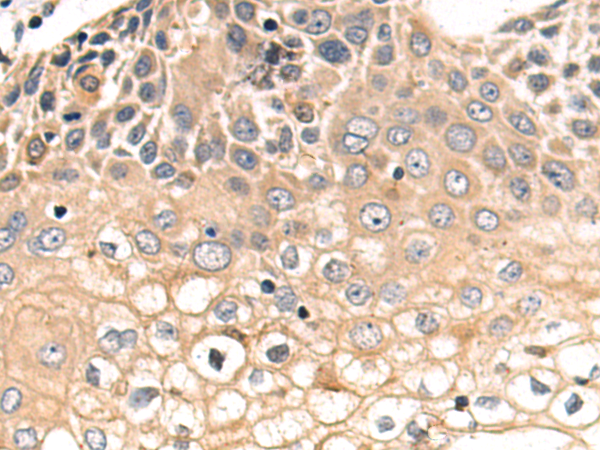
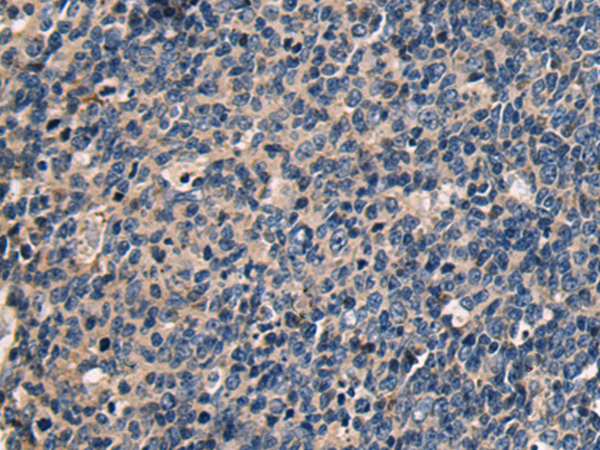
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | UEF1; ATXPC; DRIF2; C7orf6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 185 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SAMD9L |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SAMD9L抗体的3篇参考文献,基于领域内相关研究整理:
1. **文献名称**:*Germline SAMD9L mutations cause a myelodysplastic syndrome with interferon signaling dysregulation*
**作者**:Chinen Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了SAMD9L基因种系突变与骨髓增生异常综合征(MDS)的关联,通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术(使用SAMD9L特异性抗体)发现突变导致蛋白异常聚集,激活干扰素信号通路,促进细胞凋亡。
2. **文献名称**:*SAMD9L limits endosomal fusion through antiviral response components during viral infection*
**作者**:Mochizuki H, et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示SAMD9L通过调控内体膜融合抑制病毒入侵,通过抗体验证其在感染模型中的亚细胞定位变化,并发现其与抗病毒蛋白STING的相互作用。
3. **文献名称**:*SAMD9L acts as a tumor suppressor in myeloid malignancies by regulating cellular proliferation*
**作者**:Largaespada DA, et al.
**摘要**:利用SAMD9L抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现其在髓系肿瘤中表达下调,功能实验表明其缺失导致细胞周期异常和凋亡抵抗,提示其抑癌作用。
**备注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用需根据具体研究补充DOI或期刊信息。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以"SAMD9L antibody" + "应用技术"(如Western blot)为关键词检索最新论文。
The SAMD9L (Sterile Alpha Motif Domain-containing protein 9-like) gene encodes a protein involved in regulating innate immune responses, particularly interferon (IFN)-mediated pathways. It is expressed in various tissues, including immune cells, and plays roles in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and antiviral defense. SAMD9L is localized to endosomal/lysosomal membranes and acts as a scaffold protein, modulating signaling cascades. Notably, gain-of-function mutations in SAMD9L are linked to severe genetic disorders, such as infantile-onset cerebellar ataxia with sensory neuropathy (SCAAN) and familial myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), often due to dysregulated protein activity that disrupts cellular homeostasis.
SAMD9L antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, aiding research into its role in immune regulation and disease mechanisms. Commercial SAMD9L antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal regions) and validated for specificity across human and model organisms. Recent studies highlight its potential as a therapeutic target, particularly in disorders driven by hyperactive SAMD9L variants. However, challenges remain in standardizing antibody validation and interpreting its complex interactions within signaling networks. Overall, SAMD9L antibodies are indispensable for advancing insights into its dual roles in immunity and pathology.
×