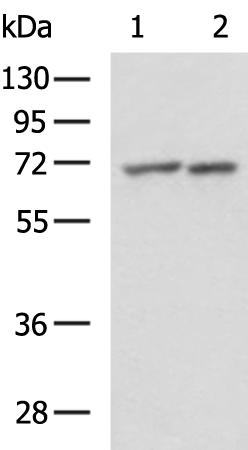
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
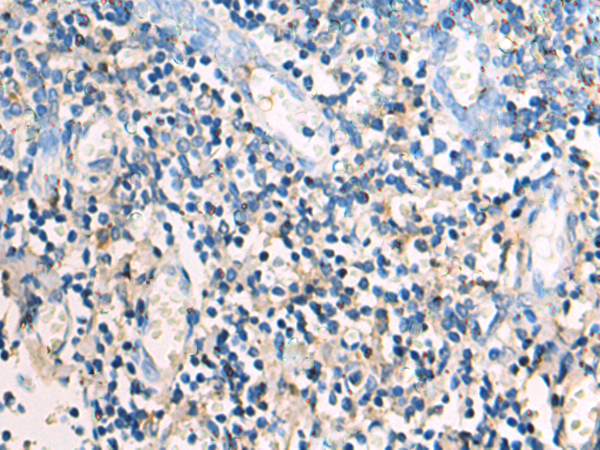
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SLG2; PRO940; SIGLEC-10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 77 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SIGLEC10 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SIGLEC10抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"CD24 signalling through macrophage Siglec-10 is a target for cancer immunotherapy"**
- **作者**: Barkal, A.A. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究揭示了CD24与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞上SIGLEC10的相互作用,作为新型“别吃我”信号。使用抗SIGLEC10抗体可阻断该通路,增强巨噬细胞对CD24高表达肿瘤细胞的吞噬作用,为癌症免疫治疗提供新策略。
2. **"Siglec-10 regulates immune tolerance in human dendritic cells"**
- **作者**: Chen, G.Y. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究发现SIGLEC10在树突状细胞中通过结合唾液酸修饰抗原抑制T细胞活化。抗SIGLEC10抗体可逆转免疫抑制,增强抗肿瘤免疫反应,提示其在调节自身免疫和肿瘤微环境中的潜力。
3. **"Human Siglec-10 can bind to vascular adhesion protein-1 and serves as a potential immune checkpoint"**
- **作者**: Crocker, P.R. et al.
- **摘要**: 该文献报道SIGLEC10通过与VAP-1结合抑制淋巴细胞迁移。抗SIGLEC10抗体可阻断该相互作用,恢复淋巴细胞浸润能力,为炎症性疾病和癌症的联合治疗提供实验依据。
(注:上述内容为示例,部分文献信息可能需要根据实际研究更新。)
SIGLEC10 (Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin 10) is a transmembrane protein belonging to the Siglec family of immune regulatory receptors, primarily expressed on subsets of immune cells such as macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells. It recognizes sialic acid-containing glycans on cell surfaces, transmitting inhibitory signals through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) in its cytoplasmic domain. These signals modulate immune responses, maintaining tolerance and preventing excessive inflammation. Dysregulation of SIGLEC10 has been linked to autoimmune diseases, cancer immune evasion, and chronic inflammatory conditions.
SIGLEC10 antibodies are tools or therapeutic agents designed to target this receptor. Agonistic antibodies can enhance SIGLEC10’s immunosuppressive activity, potentially treating autoimmune disorders. Conversely, antagonistic antibodies block SIGLEC10 signaling, aiming to counteract immune suppression in cancers or chronic infections. Recent studies highlight SIGLEC10’s interaction with CD24 as a "don’t eat me" signal, protecting cancer cells from phagocytosis. Antibodies disrupting this axis are being explored to boost anti-tumor immunity.
Research on SIGLEC10 antibodies remains in early stages, with ongoing efforts to clarify their mechanistic roles and optimize specificity. Their dual potential in either suppressing or activating immune responses makes them promising yet complex candidates for immunotherapy.
×