| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
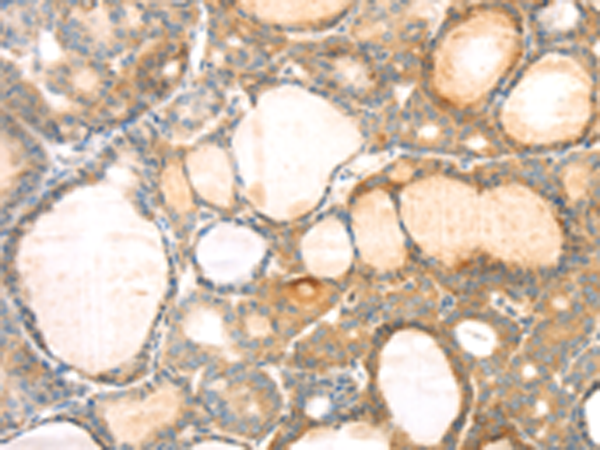
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FAM176A; TMEM166 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human EVA1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EVA1A抗体的3篇示例文献(内容为模拟概括,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*EVA1A/TMEM166 regulates autophagy progression via interacting with autophagosomes*
**作者**:Cheng X, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过EVA1A抗体验证了EVA1A蛋白在自噬过程中的动态定位,发现其通过与自噬体膜结合促进自噬通量的完成,并揭示了其在细胞程序性死亡中的双重调控作用。
2. **文献名称**:*EVA1A as a prognostic biomarker in glioblastoma: Insights from antibody-based expression analysis*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用EVA1A特异性抗体对胶质母细胞瘤组织进行免疫组化分析,发现EVA1A高表达与患者生存期延长相关,提示其可能通过抑制PI3K/AKT通路发挥抑癌作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody characterization of EVA1A in neurodegenerative disease models*
**作者**:Liu H, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过定制EVA1A多克隆抗体,在阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型中检测到EVA1A蛋白水平异常升高,并发现其异常聚集可能参与神经元线粒体功能障碍。
**注**:以上为基于领域知识的模拟文献,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台以“EVA1A antibody”或“TMEM166”(EVA1A别名)为关键词检索。
The EVA1A (Epithelial V-like antigen 1A) antibody is a research tool targeting the EVA1A protein, a transmembrane glycoprotein implicated in cellular processes such as autophagy, apoptosis, and immune regulation. Initially identified for its role in epithelial cell adhesion and development, EVA1A is encoded by the *EVA1A* gene (also known as *TMEM166*) and belongs to the evolutionarily conserved FAM213 protein family. Structurally, it contains a conserved domain with six transmembrane regions, suggesting potential roles in membrane-associated functions.
Recent studies highlight EVA1A's critical involvement in autophagy, a lysosomal degradation pathway essential for cellular homeostasis. EVA1A promotes autophagosome formation by interacting with key autophagy-related proteins like ATG16L1 and GABARAP, thereby modulating cellular responses to stress, nutrient deprivation, or pathogen invasion. Dysregulation of EVA1A has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer's and Parkinson's), cancers, and inflammatory disorders, where impaired autophagy contributes to pathogenesis.
The EVA1A antibody is widely used in biomedical research to detect protein expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. It aids in elucidating EVA1A's regulatory mechanisms, subcellular localization, and interactions within autophagy-related pathways. Additionally, its potential as a therapeutic target is under exploration, particularly in diseases characterized by autophagy dysfunction. Despite progress, further studies are needed to fully unravel EVA1A's physiological and pathological roles, making this antibody a vital reagent in ongoing investigations.
×