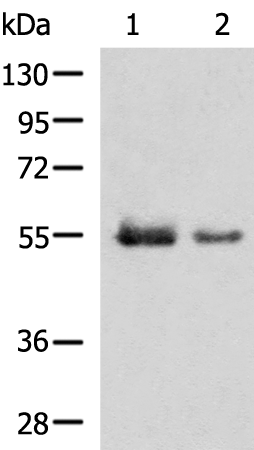
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GNT1; UGT1; UDPGT; UGT1A; UGT1D; UGT-1A; UGT-1D; UGT1.1; UGT1.4; UGT1A1; HUG-BR2; UGT1-01; UGT1-04; UGT1A4S; hUG-BR1; UDPGT 1-4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 60 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human UGT1A4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于UGT1A4抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Characterization of Human UGT1A4 Antibody Specificity and Expression in Hepatic Tissues*
**作者**: Court, M.H., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了针对UGT1A4的特异性多克隆抗体,并通过Western blot和免疫组化验证其在人肝组织中的表达。结果表明,抗体能特异性识别UGT1A4蛋白,且该酶在肝脏中呈现个体间表达差异,可能与药物代谢相关。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Immunoblot Analysis of UGT1A4 in Human Liver Microsomes: Role in Drug Glucuronidation*
**作者**: Ohno, S. and Nakajin, S.
**摘要**: 研究利用UGT1A4特异性抗体分析肝微粒体中该酶的表达水平,发现其与三环类抗抑郁药(如阿米替林)的葡萄糖醛酸化活性相关。抗体在区分UGT1A4与其他同工酶(如UGT1A3)中表现出高特异性。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Tissue-Specific Expression of UGT1A4 in Gastrointestinal Tract: Insights from Immunohistochemical Studies*
**作者**: Ehmer, P.U., et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化技术,研究揭示了UGT1A4在胃肠道(如小肠和结肠)中的区域性表达模式。抗体特异性验证显示,UGT1A4在肠上皮细胞中高表达,提示其在局部药物代谢和解毒中的作用。
---
**备注**:若需更近期或更具体的文献,建议在数据库(如PubMed)中结合关键词“UGT1A4 antibody”或“UGT1A4 immunodetection”进一步筛选。
The UGT1A4 antibody is a crucial tool for studying UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A4 (UGT1A4), an enzyme belonging to the uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) superfamily. UGT enzymes catalyze the glucuronidation of endogenous compounds (e.g., bilirubin, steroids) and xenobiotics (e.g., drugs, environmental toxins), enhancing their water solubility for excretion. UGT1A4. encoded by the UGT1A gene complex on chromosome 2q37. is primarily expressed in the liver, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys. It specifically metabolizes amines and tertiary amines, including drugs like antidepressants (e.g., imipramine) and antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine).
Antibodies targeting UGT1A4 enable researchers to detect and quantify its expression in tissues or cell lines, aiding studies on interindividual variability in drug metabolism, enzyme regulation, and disease associations. For example, altered UGT1A4 activity has been linked to drug resistance, toxicity, or efficacy in chemotherapy. Commercial UGT1A4 antibodies are typically monoclonal or polyclonal, validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or ELISA. Their specificity is critical due to high homology among UGT1A isoforms.
Research using UGT1A4 antibodies contributes to understanding genetic polymorphisms (e.g., UGT1A4*3) affecting drug responses and personalized medicine. Additionally, they help explore UGT1A4's role in cancers, where dysregulated glucuronidation may influence tumor progression or drug resistance. Proper validation with controls (e.g., knockout cells) ensures accurate interpretation in experimental models.
×