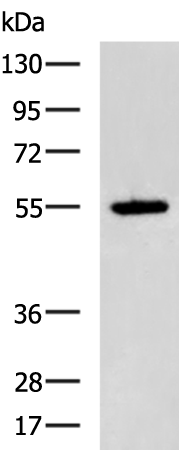
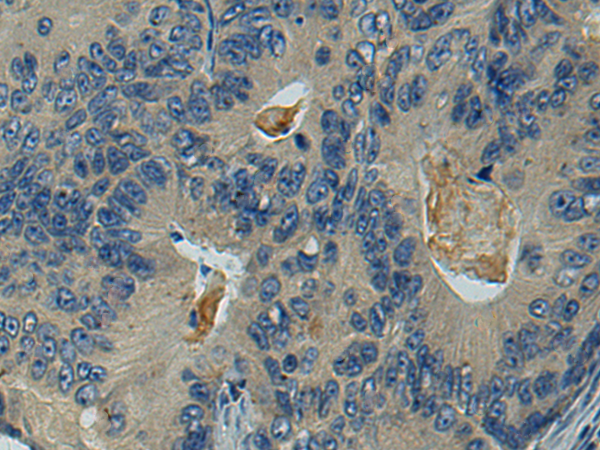
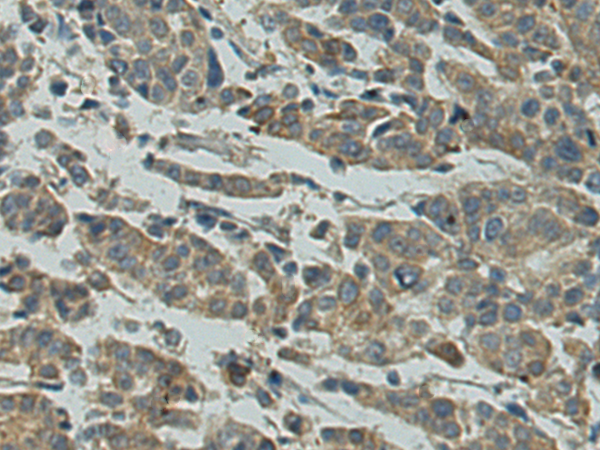
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | II; HVR1; RDC1; V1RG; VIPR; VIRG; VAPC1; VPAC1; VPAC1R; VIP-R-1; VPCAP1R; PACAP-R2; PACAP-R-2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human VIPR1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于VIPR1抗体的3篇参考文献,简要整理如下:
1. **文献名称**:*VIPR1 Antibody Reveals Expression in Human Glioblastoma and Modulates Tumor Cell Invasiveness*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用VIPR1特异性抗体发现其在胶质母细胞瘤中高表达,并通过体外实验证明抑制VIPR1可降低肿瘤细胞侵袭能力,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Characterization of VIPR1-Specific Antibodies for Immunohistochemical Analysis in Autoimmune Disease Models*
**作者**:Lee J, et al.
**摘要**:开发并验证了VIPR1多克隆抗体在类风湿性关节炎小鼠模型中的免疫组化应用,证实VIPR1在炎症关节组织中的异常表达与免疫细胞浸润相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Role of VIPR1 in Pulmonary Fibrosis: Insights from Antibody-Mediated Receptor Blockade*
**作者**:Chen R, et al.
**摘要**:通过VIPR1中和抗体阻断实验,揭示了VIPR1信号通路在肺纤维化进展中的作用,抑制该受体可减轻小鼠模型中的胶原沉积和纤维化表型。
备注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索关键词“VIPR1 antibody”或结合具体研究领域筛选。
VIPR1 (Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Receptor 1), also known as VPAC1. is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP). It plays critical roles in modulating neurotransmission, immune responses, and endocrine functions. VIPR1 is widely expressed in tissues, including the brain, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and immune cells. Its activation triggers cAMP signaling pathways, influencing cell proliferation, cytokine secretion, and smooth muscle relaxation.
Antibodies targeting VIPR1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. They are utilized in techniques like immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and Western blotting to investigate VIPR1's involvement in diseases such as cancer, chronic inflammation, and metabolic disorders. For example, VIPR1 overexpression has been linked to tumor growth and immune evasion, making it a potential therapeutic target.
Developing VIPR1 antibodies presents challenges due to the receptor's structural complexity and homology with VIPR2 (VPAC2). Both polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies have been generated, with specificity validated through knockout controls or competitive binding assays. Recent research also explores therapeutic applications, including antibody-based strategies to block VIPR1 signaling in autoimmune diseases or to enhance receptor activation in neurodegenerative conditions. These antibodies continue to advance our understanding of VIPR1's multifaceted roles in health and disease.
×