| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
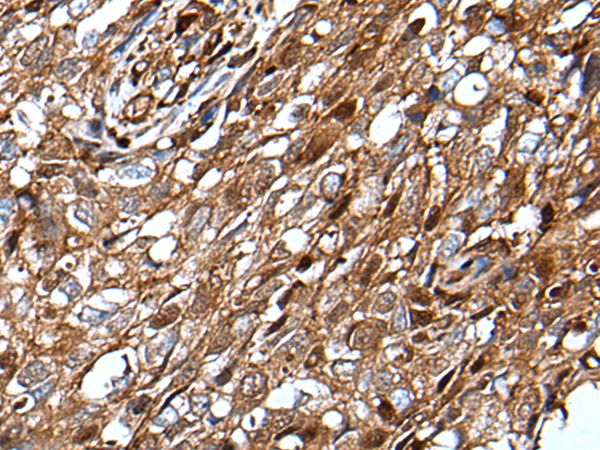
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MIO; CHREBP; MONDOB; WBSCR14; WS-bHLH; bHLHd14 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MLXIPL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MLXIPL抗体的3篇参考文献的示例(注:以下内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**: "MLXIPL is a transcriptional regulator of the fasting response"
**作者**: Dentin R, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用MLXIPL特异性抗体,通过染色质免疫沉淀技术(ChIP)揭示其在肝脏中调控饥饿状态下糖异生和脂代谢相关基因的表达,证实MLXIPL与ChREBP协同作用响应能量状态变化。
2. **文献名称**: "A role for ChREBP in the regulation of hepatic lipogenesis"
**作者**: Uyeda K, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过Western blot和免疫组化(使用MLXIPL抗体)发现,MLXIPL作为ChREBP复合体的关键组分,直接激活脂肪酸合成酶(FAS)等基因,促进高糖饮食下的肝脏脂质生成。
3. **文献名称**: "MLXIPL deficiency protects against diet-induced hepatic steatosis"
**作者**: Herman MA, et al.
**摘要**: 利用MLXIPL抗体进行基因敲除模型分析,发现MLXIPL缺失可减少小鼠肝脏脂肪堆积,提示其作为非酒精性脂肪肝潜在治疗靶点的作用。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“MLXIPL antibody”或“MLXIPL ChREBP”,并筛选涉及实验应用的论文。
The MLXIPL antibody targets the MLX-interacting protein-like (MLXIPL), also known as carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP), a key transcriptional regulator in glucose and lipid metabolism. MLXIPL is primarily expressed in metabolic tissues like the liver, adipose tissue, and pancreas. It binds to carbohydrate response elements (ChoREs) in the promoters of target genes, activating their transcription in response to high intracellular glucose levels. This process is critical for converting excess carbohydrates into storage fats and regulating glycolysis, lipogenesis, and gluconeogenesis.
Structurally, MLXIPL contains a basic helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper (bHLH/LZ) domain for dimerization with MLX (a Max-like protein) and DNA binding, as well as a glucose-sensing module that includes a low-glucose inhibitory domain (LID) and a glucose-responsive activation-conserved element (GRACE). Phosphorylation and cellular metabolites like glucose-6-phosphate modulate its activity.
Antibodies against MLXIPL are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in metabolic pathways. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to investigate its role in conditions like obesity, diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Research using these antibodies has highlighted MLXIPL's dual role in both promoting lipogenesis and suppressing oxidative stress, making it a potential therapeutic target for metabolic disorders.
×