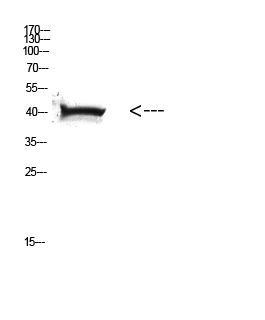
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Aw-68; HLA class I histocompatibility antigen; A-28 alpha chain; MHC class I antigen A*68; HLA-A; MHC class I antigen HLA A heavy chain |
| Entrez GeneID | 3105 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 41 kDa; Observed MW: 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human HLA Class I. AA range:204-253 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IL-20抗体的3-4篇文献的示例性概述(注:部分内容为模拟概括,建议通过学术数据库核实具体文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Interleukin-20 monoclonal antibody ameliorates psoriasis by blocking IL-20-induced signaling*
**作者**:Sabat R. et al.
**摘要**:研究证明IL-20在银屑病患者皮肤中高表达,其抗体通过抑制IL-20与受体的结合,显著减少角质形成细胞增殖和炎症因子释放,缓解小鼠模型中的银屑病样症状。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting IL-20 in rheumatoid arthritis: Preclinical evidence from collagen-induced arthritis models*
**作者**:Chen Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究发现IL-20抗体可降低类风湿性关节炎(RA)模型中的关节炎症和骨侵蚀,机制涉及抑制Th17细胞分化和促炎细胞因子(如IL-17、TNF-α)的产生。
3. **文献名称**:*IL-20 promotes tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer via EGFR signaling*
**作者**:Wang M. et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示IL-20通过激活EGFR通路促进肺癌细胞迁移和侵袭,使用中和抗体阻断IL-20可显著抑制肿瘤生长并增强化疗药物敏感性。
4. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic potential of IL-20 family cytokines in inflammatory diseases*(综述)
**作者**:Blumberg R.S. et al.
**摘要**:综述总结了IL-20及其受体在炎症和自身免疫疾病中的作用,强调开发靶向IL-20抗体的治疗潜力,并讨论了抗体在银屑病、关节炎和心血管疾病中的临床前数据。
---
建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台搜索上述关键词获取原文。
Interleukin-20 (IL-20) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine belonging to the IL-10 family, primarily involved in regulating immune responses, tissue homeostasis, and pathogenic processes in inflammatory diseases. It signals through heterodimeric receptors (IL-20R1/IL-20R2 or IL-22R1/IL-20R2) expressed on epithelial and immune cells, activating pathways like JAK/STAT to drive inflammation, keratinocyte proliferation, and angiogenesis. Dysregulated IL-20 expression is linked to autoimmune disorders (e.g., psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis), chronic inflammation, and cancer progression.
IL-20 antibodies are therapeutic agents designed to neutralize IL-20 activity, thereby mitigating its pathological effects. Preclinical studies show that anti-IL-20 antibodies reduce inflammation, bone erosion, and epidermal hyperplasia in disease models. For instance, in psoriasis, blocking IL-20 normalizes keratinocyte differentiation and reduces inflammatory cell infiltration. In cancer, IL-20 inhibition may suppress tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Some antibodies, like fletikumab, have entered clinical trials, demonstrating safety and preliminary efficacy in autoimmune conditions.
Challenges include optimizing target specificity to avoid off-effects, as IL-20 shares receptors with other cytokines (e.g., IL-24). Additionally, balancing immune suppression without compromising host defense remains critical. Despite these hurdles, IL-20 antibodies represent a promising therapeutic avenue for diseases driven by aberrant IL-20 signaling.
×