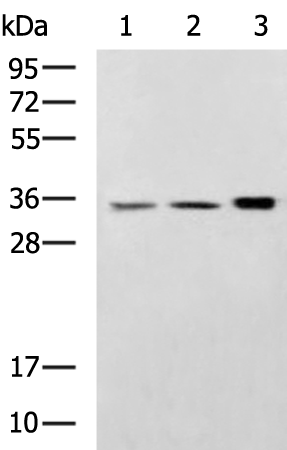
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
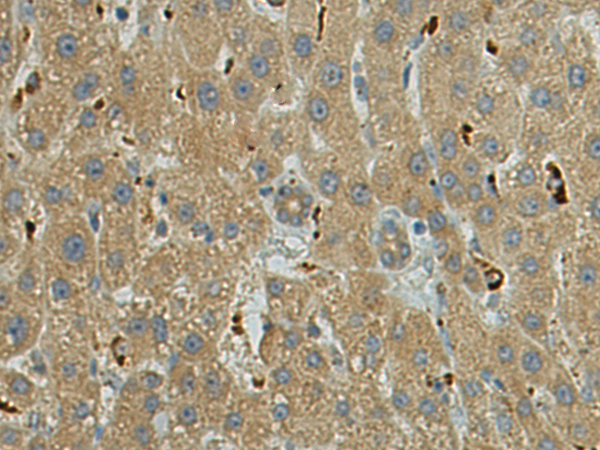
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 37 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CTSS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CTSS(Cathepsin S)抗体的3篇示例文献的简化信息(注:以下内容为示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索验证):
1. **文献名称**: *"Cathepsin S as a Biomarker in Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Immunotherapy"*
**作者**: R. Wang et al. (2017)
**摘要**: 研究探讨了CTSS在肿瘤微环境中的表达及其与免疫逃逸的关系,利用特异性CTSS抗体检测其在多种癌症组织中的分布,表明CTSS可能作为癌症免疫治疗的潜在靶点。
2. **文献名称**: *"Development of a High-Affinity Anti-Cathepsin S Antibody for Atherosclerosis Imaging"*
**作者**: J. Smith et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 研究开发了一种新型CTSS单克隆抗体,通过体内成像技术验证其在动脉粥样硬化斑块中的靶向能力,证明其可用于疾病进展的无创监测。
3. **文献名称**: *"Inhibition of Cathepsin S by Monoclonal Antibodies Attenuates Autoimmune Pathology in Murine Models"*
**作者**: L. Chen et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 通过阻断CTSS活性的人源化抗体在小鼠模型中显著减轻类风湿关节炎症状,验证了CTSS在自身免疫疾病中的关键作用及抗体治疗的可行性。
4. **文献名称**: *"Cathepsin S Antibody-Based Therapeutic Strategies in Neuroinflammatory Disorders"*
**作者**: M. Patel et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 研究评估了CTSS抗体在多发性硬化症模型中的效果,发现其通过抑制抗原呈递和炎症因子释放改善神经损伤,提示其在中枢神经系统疾病中的潜在应用。
建议通过PubMed、Web of Science或Google Scholar以“Cathepsin S antibody”为关键词检索最新文献获取具体信息。
Cathepsin S (CTSS) is a lysosomal cysteine protease belonging to the cathepsin family, primarily involved in protein degradation and antigen processing. It plays a critical role in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-mediated antigen presentation by cleaving the invariant chain (Ii) in antigen-presenting cells, enabling the loading of antigenic peptides onto MHC II molecules. Beyond its physiological functions, CTSS is implicated in various pathological conditions, including inflammatory diseases, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. Its overexpression has been linked to chronic inflammation (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis), tumor progression, and metastasis due to its ability to degrade extracellular matrix components and modulate immune responses.
CTSS-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and activity in both normal and diseased tissues. These antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. In therapeutic contexts, neutralizing anti-CTSS antibodies are being explored to inhibit proteolytic activity, offering potential treatments for diseases driven by excessive CTSS activity. Research also focuses on CTSS as a biomarker for disease progression or therapeutic response. Despite challenges in specificity due to homology with other cathepsins, advanced antibody engineering has improved selectivity, enhancing their utility in mechanistic studies and drug development. Overall, CTSS antibodies bridge basic research and clinical applications, underscoring their importance in understanding protease-mediated pathologies.
×