| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
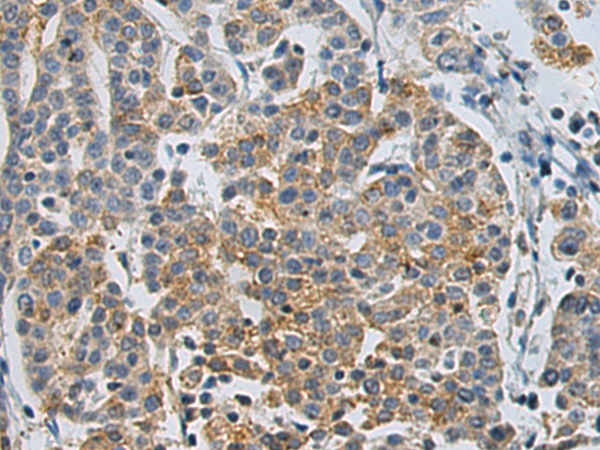
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CEG1; EGFR-5; C14orf27 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CLEC14A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CLEC14A抗体的文献概览(文献名称、作者及摘要概括):
1. **文献名称**: *CLEC14A selectively regulates VEGFR-2 and NRP1 signaling in endothelial cells*
**作者**: Miyazaki T. et al. (2015)
**摘要**: 研究揭示CLEC14A在肿瘤血管内皮细胞中特异性高表达,并通过抗体阻断实验证实其通过调控VEGFR-2和NRP1信号通路抑制血管生成,提示其作为抗血管治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**: *A human monoclonal antibody targeting CLEC14A inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth*
**作者**: Hoang K.C. et al. (2016)
**摘要**: 报道一种靶向CLEC14A的单克隆抗体的开发,该抗体通过抑制内皮细胞迁移和管腔形成显著减少肿瘤血管密度,并在小鼠模型中降低肿瘤体积,验证了其抗肿瘤效果。
3. **文献名称**: *CLEC14A-targeted antibody-drug conjugate for tumor-specific therapy*
**作者**: Yoo S.Y. et al. (2017)
**摘要**: 研究利用抗CLEC14A抗体构建抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),证实其能选择性递送化疗药物至肿瘤血管,显著增强疗效并降低全身毒性,为精准治疗提供新策略。
以上文献集中于CLEC14A抗体的功能机制、治疗应用及靶向递送系统的开发。
CLEC14A (C-type lectin domain family 14 member A) is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the C-type lectin superfamily, which is predominantly expressed on vascular endothelial cells. It plays a critical role in angiogenesis, particularly in tumor-associated blood vessel formation. Research has shown that CLEC14A is selectively overexpressed in tumor endothelial cells compared to normal tissues, making it a promising target for anti-angiogenic therapies and cancer diagnostics. Its extracellular C-type lectin domain mediates interactions with unknown ligands, potentially regulating endothelial cell migration, proliferation, and vessel stabilization.
CLEC14A antibodies are tools developed to study the protein's function and therapeutic potential. These antibodies, often monoclonal or polyclonal, enable detection of CLEC14A in assays like immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and Western blot. Some therapeutic antibodies are engineered to block CLEC14A-mediated signaling, aiming to disrupt pathological angiogenesis in cancers. Studies suggest that targeting CLEC14A with antibodies may inhibit tumor growth by normalizing abnormal vasculature or inducing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).
Commercial CLEC14A antibodies are available for research, with validation in specific applications varying by clone and epitope specificity. Challenges include ensuring binding specificity due to potential glycosylation interference and cross-reactivity with other lectin family proteins. Ongoing research explores CLEC14A's role in vascular biology and its utility as a biomarker or therapeutic target in oncology.
×