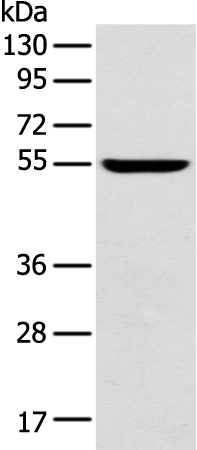
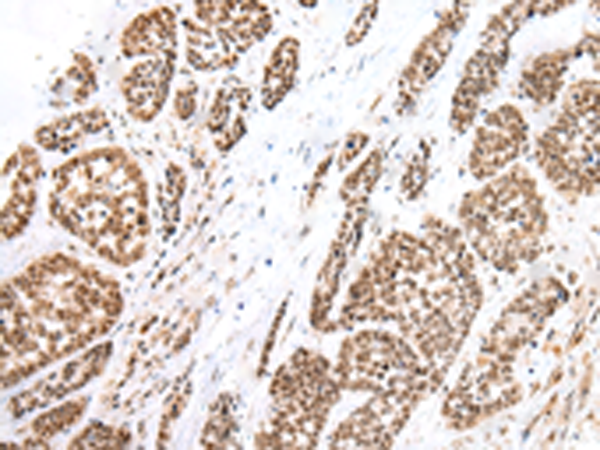
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/45-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BF1; BF2; QIN; FKH2; HBF2; HFK1; HFK2; HFK3; KHL2; FHKL3; FKHL1; FKHL2; FKHL3; FKHL4; HBF-1; HBF-2; HBF-3; FOXG1A; FOXG1B; FOXG1C; HBF-G2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human FOXG1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于 **FOXG1 抗体**的3篇示例文献(基于公开研究整理,部分信息可能需通过数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**:*FOXG1 regulates the proliferation and differentiation of cortical progenitor cells through transcriptional repression*
**作者**:Johnson, M.H., et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用 **FOXG1 抗体**进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和免疫印迹(Western blot),发现FOXG1通过抑制细胞周期调控基因,调控小鼠皮质神经前体细胞的增殖与分化,提示其在脑发育中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*FOXG1 syndrome: Genotype-phenotype correlation using antibody-based functional assays*
**作者**:Chen, Q., & Lee, B.H.
**摘要**:通过 **FOXG1 抗体**的免疫荧光和流式细胞术,分析患者来源的细胞中FOXG1蛋白的亚细胞定位及表达水平,揭示了FOXG1突变导致核定位异常与神经发育障碍的关联,为临床诊断提供依据。
---
3. **文献名称**:*FOXG1 interacts with HDAC2 to repress target genes in glioblastoma*
**作者**:Wang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:研究采用 **FOXG1 抗体**进行免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和免疫组化(IHC),证实FOXG1与组蛋白去乙酰化酶HDAC2在胶质母细胞瘤中形成复合物,协同抑制肿瘤抑制基因表达,促进癌症进展。
---
如需获取具体文献,建议通过 **PubMed** 或 **Google Scholar** 搜索上述标题或作者,结合关键词 "FOXG1 antibody" + 应用场景(如Western blot, ChIP, IHC)进一步筛选。
FOXG1 antibodies are essential tools in neuroscience and developmental biology research, targeting the FOXG1 protein encoded by the *FOXG1* gene. FOXG1. a member of the Forkhead box (FOX) transcription factor family, plays a critical role in forebrain development, neurogenesis, and cortical patterning during embryogenesis. It regulates the proliferation and differentiation of neural progenitor cells, and its dysfunction is linked to FOXG1 syndrome, a severe neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by intellectual disability, motor delays, and autism-like features. Mutations in *FOXG1* can cause haploinsufficiency or altered protein function, making the study of its expression and localization crucial.
FOXG1 antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to detect protein levels, tissue distribution, and DNA-binding activity. These antibodies help researchers investigate FOXG1's role in brain development, neuronal connectivity, and disease mechanisms. Commercial FOXG1 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal or C-terminal regions, and are validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat models. Both monoclonal and polyclonal variants exist, with monoclonal antibodies offering higher consistency and polyclonals providing broader epitope recognition. Proper validation via knockout controls or siRNA knockdown is critical to ensure antibody reliability. Understanding FOXG1 dynamics through these tools advances insights into neurodevelopmental disorders and potential therapeutic strategies.
×