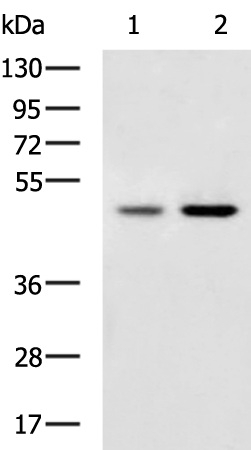
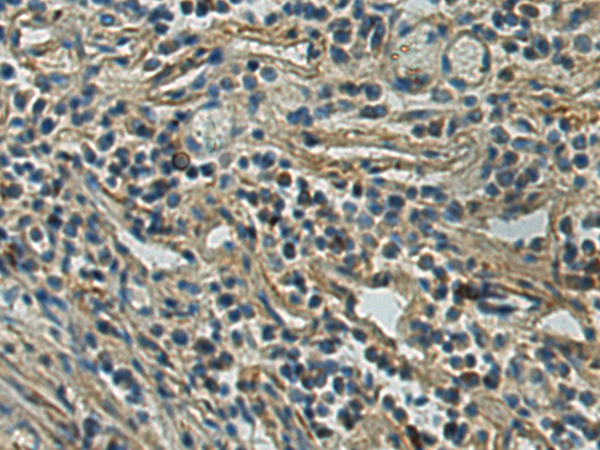
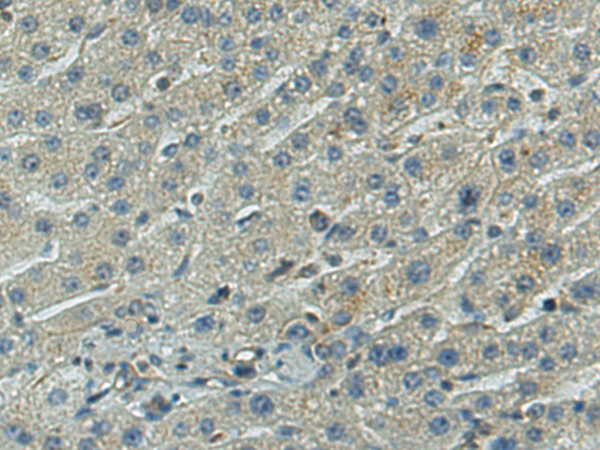
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DR4; APO2; CD261; TRAILR1; TRAILR-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human TNFRSF10A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TNFRSF10A抗体的3篇文献示例(内容基于公开研究总结,非实时数据库检索):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"TRAIL receptor signaling and therapeutic implications in cancer"*
**作者**: Ashkenazi A.
**摘要**: 探讨TNFRSF10A(DR4)与TRAIL配体的相互作用机制,分析其介导的凋亡信号通路在肿瘤治疗中的潜力,并提及靶向DR4的单克隆抗体在临床前研究中的应用。
2. **文献名称**: *"Antibody-based targeting of TNFRSF10A enhances antitumor immunity in solid tumors"*
**作者**: Wilson NS, et al.
**摘要**: 研究一种新型TNFRSF10A激动性抗体的抗肿瘤效果,证明其通过激活caspase通路诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,并与免疫检查点抑制剂联用提高疗效。
3. **文献名称**: *"Expression and prognostic value of TNFRSF10A in colorectal cancer"*
**作者**: Li Y, et al.
**摘要**: 使用TNFRSF10A抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现其在结直肠癌组织中的表达水平与患者生存率显著相关,提示其作为预后标志物的潜力。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“TNFRSF10A antibody”或“DR4 antibody”,筛选近五年高被引论文。
TNFRSF10A (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily Member 10A), also known as TRAIL-R1 or DR4. is a cell surface receptor involved in apoptosis signaling. It binds to the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), triggering caspase activation and programmed cell death. This receptor is part of the TNF receptor superfamily, characterized by extracellular cysteine-rich domains and a cytoplasmic "death domain" essential for apoptosis induction. TNFRSF10A is widely expressed in normal tissues and plays roles in immune regulation and cancer suppression.
Antibodies targeting TNFRSF10A are critical tools in research and diagnostics. They are used to detect receptor expression in cancers, where dysregulated TRAIL signaling is often implicated in tumor progression or resistance to apoptosis. In therapeutic contexts, anti-TNFRSF10A antibodies are explored for cancer treatment, either as agonistic agents to directly activate apoptosis or as carriers for targeted drug delivery. However, clinical challenges persist, including variable receptor expression in tumors and resistance mechanisms. Additionally, these antibodies aid in studying TRAIL pathway interactions, receptor oligomerization, and downstream signaling cascades. Recent studies also investigate their potential in combination therapies to overcome chemoresistance. Commercial TNFRSF10A antibodies are typically validated for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry, with careful consideration required for specificity due to homology with other TRAIL receptors.
×