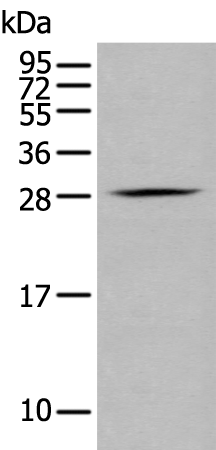
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MET1; LMET1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GZMM |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GZMM(Granzyme M)抗体的3篇参考文献摘要,供参考:
---
1. **标题**: *Granzyme M is a regulatory protease for inducible IL-6 production and apoptosis*
**作者**: Kelly JM 等
**摘要**: 研究利用GZMM特异性抗体,揭示了GZMM在NK细胞中通过调控IL-6信号通路参与炎症反应,并发现其通过非典型凋亡途径影响靶细胞死亡。
2. **标题**: *Granzyme M mediates a novel pathway of DNA damage-induced apoptosis in myeloma cells*
**作者**: de Bruin EC 等
**摘要**: 通过抗GZMM抗体的阻断实验,证明GZMM在多发性骨髓瘤细胞中通过激活DNA损伤通路诱导凋亡,为靶向治疗提供了潜在策略。
3. **标题**: *Human granzyme M is a protease responsible for the induction of programmed cell death*
**作者**: Bovenschen N 等
**摘要**: 利用重组GZMM蛋白及抗体验证其蛋白酶活性,证实GZMM通过裂解特定底物触发肿瘤细胞凋亡,并与其他颗粒酶功能差异对比。
---
**说明**:以上文献聚焦于GZMM在免疫杀伤、炎症调节及疾病中的作用,抗体多用于功能验证(如Western blot、流式细胞术)或机制研究。实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Sci-Hub核对原文。
The GZMM antibody targets Granzyme M (GZMM), a serine protease in the granzyme family, primarily expressed by natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. GZMM is stored in cytotoxic granules and released upon immune cell activation to induce apoptosis in infected or malignant cells. Unlike the well-characterized Granzyme B, which activates caspase-dependent apoptosis, GZMM triggers cell death through caspase-independent pathways, such as cleaving nuclear or mitochondrial proteins, and may contribute to inflammation regulation.
GZMM antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in immune responses. They are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to explore GZMM’s role in infections, cancer immunosurveillance, and autoimmune disorders. Research suggests GZMM may influence tumor progression, viral clearance, and inflammatory diseases, but its mechanisms remain less understood compared to other granzymes.
These antibodies also aid in developing therapeutic strategies, such as enhancing cytotoxic activity in immunotherapy or modulating excessive inflammation. Challenges include ensuring antibody specificity due to structural similarities among granzymes. Overall, GZMM antibodies provide insights into immune cell biology and potential clinical applications, bridging gaps in understanding cytotoxic lymphocyte functions.
×