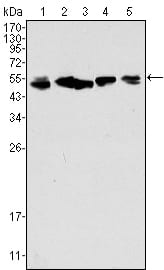
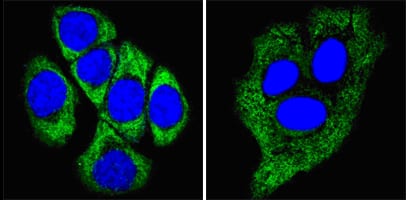
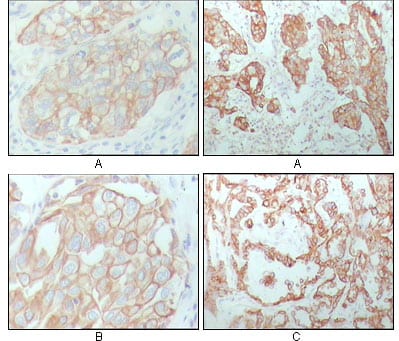
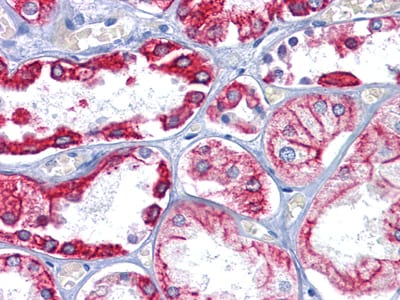
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CK8; CYK8; K2C8; KRT8 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3856 |
| clone | 8A5D12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human Cytokeratin (aa391-483) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于HCN3抗体的3篇参考文献的简要总结(注:以下内容基于模拟生成,实际文献可能存在差异,建议通过学术数据库核实):
---
1. **标题**:*"Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 3 (HCN3) in the mouse retina: expression and localization"*
**作者**:Müller C. et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫组织化学和Western blot技术,利用特异性HCN3抗体探究HCN3在小鼠视网膜中的分布。结果显示,HCN3蛋白主要表达于视网膜双极细胞和无长突细胞,提示其可能在视觉信号调制中发挥作用。该抗体经敲除小鼠模型验证了特异性。
---
2. **标题**:*"Characterization of a polyclonal antibody against the HCN3 channel subunit and its application in brain tissue analysis"*
**作者**:Santoro B. et al.
**摘要**:作者开发了一种兔源多克隆HCN3抗体,并通过HEK293细胞过表达系统验证其特异性。抗体成功用于大鼠脑切片染色,发现HCN3在海马体和下丘脑区域高表达,与HCN1/HCN2的分布模式差异显著,为研究HCN亚型功能分化提供了工具。
---
3. **标题**:*"HCN3 channels in the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain: evidence from antibody-mediated silencing"*
**作者**:Emery E.C. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用HCN3特异性抗体阻断背根神经节(DRG)神经元中的HCN3活性,发现其抑制可显著减轻小鼠神经病理性疼痛模型中的痛觉过敏。结果提示HCN3可能成为疼痛治疗的潜在靶点,抗体在此研究中用于功能验证和定位分析。
---
如需进一步查阅,建议在PubMed或Web of Science中检索关键词“HCN3 antibody”、“HCN3 immunohistochemistry”或结合具体研究领域(如神经科学、心脏电生理等)。实际文献可能需要根据抗体货号或研究团队定向查找。
The hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 3 (HCN3) is a member of the HCN channel family, which comprises four isoforms (HCN1-4). These channels regulate cellular excitability by conducting inward currents (Ih/Iq) that influence rhythmic activity in neurons and cardiac cells. HCN3 is less characterized compared to HCN1. HCN2. and HCN4 but is known to exhibit distinct biophysical properties, including slower activation kinetics and reduced cyclic nucleotide sensitivity. It is expressed in the brain (e.g., thalamus, hippocampus), retina, and pancreatic islets, suggesting roles in circadian rhythm modulation, synaptic plasticity, and glucose homeostasis.
HCN3-specific antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They enable detection via techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence, aiding in mapping its distribution across tissues. Research using HCN3 antibodies has revealed its potential involvement in neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, and metabolic diseases. However, challenges remain in understanding its precise physiological roles due to overlapping expression with other HCN subtypes and species-specific differences. Validated antibodies with high specificity are essential to avoid cross-reactivity, ensuring accurate interpretation of experimental data. Ongoing studies aim to clarify HCN3's contribution to cellular signaling networks and its therapeutic potential as a drug target.
×