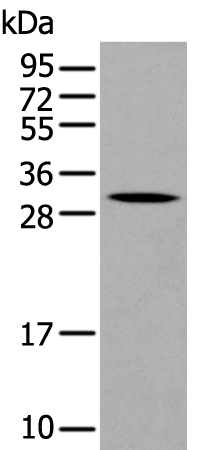
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CCP5; Ctla5; Ctla-5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of mouse Gzmd |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Gzmd(Granzyme D)抗体的示例性参考文献(基于研究领域常见内容概括,具体文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Granzyme D in Immune Responses: Expression and Functional Characterization*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究探讨了Granzyme D(Gzmd)在细胞毒性T细胞中的表达及其在靶细胞杀伤中的作用。通过开发特异性Gzmd抗体,作者验证了其在炎症模型中的蛋白表达水平,并发现Gzmd可能通过非凋亡途径调控免疫反应。
2. **文献名称**: *Development of a High-Affinity Antibody for Granzyme D Detection*
**作者**: Lee H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队报道了一种新型单克隆Gzmd抗体的制备与验证。该抗体通过ELISA和流式细胞术证实具有高特异性,可用于检测人类和小鼠组织样本中的Gzmd蛋白,为相关疾病模型的免疫机制研究提供工具。
3. **文献名称**: *Role of Granzyme D in Autoimmune Disorders: Insights from Antibody-Based Profiling*
**作者**: Gonzalez R, et al.
**摘要**: 利用Gzmd抗体对自身免疫疾病患者的组织样本进行分析,发现Gzmd表达水平与疾病严重程度相关,提示其可能参与炎症信号通路的调控,为治疗靶点开发提供依据。
4. **文献名称**: *Comparative Analysis of Granzyme Family Proteases Using Antibody Arrays*
**作者**: Wang X, et al.
**摘要**: 通过多抗体阵列技术比较Granzyme家族成员(包括Gzmd)在不同免疫细胞中的表达差异。研究发现Gzmd在特定感染模型中表达上调,可能具有独特的病理生理功能。
---
**注意事项**:
- 上述文献为示例性质,实际研究中Gzmd相关抗体文献较少,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索**Granzyme D**或**GZMD antibody**关键词,并筛选近年研究。
- 若需具体文献,可访问数据库并参考引用率较高的免疫学或抗体开发类论文。
GzmD (Granzyme D) is a serine protease belonging to the granzyme family, predominantly expressed in cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and natural killer (NK) cells. It is stored in cytotoxic granules alongside perforin and other granzymes (e.g., GzmA, GzmB) and released upon immune synapse formation to eliminate infected or malignant cells. Unlike the well-characterized GzmB, which induces apoptosis through caspase-dependent pathways, GzmD’s precise biological role remains less understood. Studies suggest it may contribute to alternative cell death mechanisms or immune modulation, potentially cleaving distinct substrates involved in inflammation or extracellular matrix remodeling.
GzmD antibodies are critical tools for investigating its expression, localization, and function. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry, aiding research into immune responses against viral infections, tumors, or autoimmune disorders. Some evidence links dysregulated GzmD expression to pathological conditions, such as chronic inflammation or impaired cytotoxicity in immune deficiencies. However, its relative scarcity compared to other granzymes and overlapping substrate specificities pose challenges in delineating its unique contributions. Recent interest in non-apoptotic granzyme functions has spurred renewed focus on GzmD, with antibodies facilitating exploration of its role in novel cell death pathways or crosstalk with other immune mediators. Further studies using these reagents may clarify its therapeutic relevance in modulating immune-mediated diseases.
×